This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
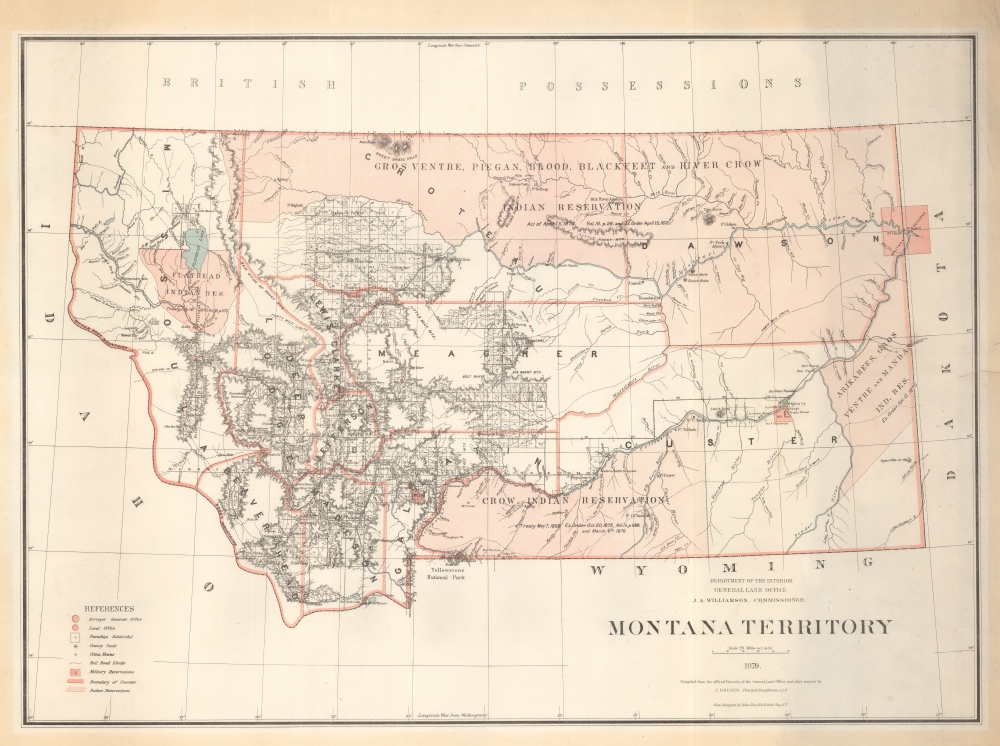
1879 General Land Office Map of Montana Territory
MontanaTerritory-glo-1879
Title
1879 (dated) 24 x 32.25 in (60.96 x 81.915 cm) 1 : 1267200
Description
A Closer Look
The map covers territorial Montana along the same borders that would in 1889 become the state of Montana. The map is dominated by vast American Indian reservations, particularly in the northern and western parts of the territory. Human and natural geography is illustrated, with dense topography and an embryonic county structure. Yellowstone National Park, founded in 1872, is named at bottom center. In the upper right, straddling Montana and Dakota, is the Fort Buford Military Reservation - it was here that in 1881, two years after this map was printed, that Sitting Bull, hungry and desperate, would surrender. Bufford was decommissioned in 1895.Historical Context
Montana Territory was established in 1864. By 1879, when this map was issued, Montana was rapidly evolving, shaped by the influences of mining, ranching, and the Northern Pacific Railway. This era saw a boom in mining, especially with the discovery of gold and silver, which attracted a surge of settlers and prospectors. Towns sprang up around mining camps, leading to a diverse population influx. The construction of the Northern Pacific Railway was also underway, having reached Missoula, significantly impacting trade and migration. Ranching also began to take hold, capitalizing on the vast open spaces ideal for cattle grazing. Despite these developments, Montana retained its rugged, frontier nature, with Native American tribes, such as the Blackfoot, Crow, and Cheyenne, playing a significant role in the region's dynamics.Publication History and Census
This map was prepared from documents at the General Land Office in 1879 by Charles Roeser under the direction of J. A. Williamson. It was engraved and printed in New York by Julius Bien. It is an updated version of a map first issued in 1876. We see examples in OCLC cataloged in about 20 libraries, although many are later editions, and some are digital resources populated from the Library of Congress example.CartographerS
The General Land Office (GLO) (1812 - 1946) was an independent agency of the United States government responsible for public domain lands in the United States. Created in 1812, it took over functions previously conducted by the Department of the Treasury. The GLO oversaw the surveying, platting, and sale of public lands in the western United States. It also administered the Preemption Act of 1841, which allowed individuals who were already living on federal land to purchase up to 160 acres of land before it was offered for sale to the general public, if they met certain requirements. Following the passage of the Homestead Act in 1862, which was also administered by the GLO, claims under the Preemption Act sharply decreased. The GLO became a part of the newly-created Department of the Interior in 1849. In 1891 Grover Cleveland and Congress created 17 forest reserves, due to public concern over forest conservation, which were initially managed by the GLO, until they were transferred to the Forest Service in 1905. In 1946 the Government Land Office was merged with the United States Grazing Service to become the Bureau of Land Management. Today the Bureau of Land Management administers the roughly 246 million acres of public land remaining under federal ownership. More by this mapmaker...
Charles 'Karl' Richard Roeser (December 15, 1842 - June 23, 1893) was a Prussian-American surveyor and draftsman working with the U.S. General Land Office in the second half of the 19th century. Roeser was born in Merseburg, Saalekreis, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, but emigrated to the United States as a child with his family, settling in Wisconsin. In 1857-61 he took a degree in engineering from Lawrence University, Wisconsin, then went on to take a degree in law from Columbia. Shortly after the American Civil War (1861 - 1865) he entered public service as the Chief Draftsman of the General Land Office. He issued an 1875 map of the United States and an 1876 Centennial atlas of the United States, the Geographical and political atlas of the states and territories of the United States of America. He transferred to the Topographer's Office under Postmaster General Howe in 1882 with the mission to fully reorganize and modernize that department's mapping resources. He maintained the position of Chief Topographer to the Post Office until his death in Washington D. C. in 1893. Learn More...
Julius (Julien) Bien (September 27, 1826 - December 21, 1909) was a German-Jewish lithographer and engraver based in New York City. Bien was born in Naumburg, Germany. He was educated at the Academy of Fine Arts, Cassell and at Städel's Institute, Frankfurt-am-Main. Following the suppression of the anti-autocratic German Revolutions of 1848, Bien, who participated in the pan-German movement, found himself out of favor in his home country and joined the mass German immigration to the United States. Bien can be found in New York as early as 1849. He established the New York Lithographing, Engraving & Printing Company in New York that focused on the emergent chromo-lithograph process - a method of printing color using lithographic plates. His work drew the attention of the U.S. Government Printing Office which contracted him to produce countless government maps and surveys, including the Pacific Railroad Surveys, the census, numerous coast surveys, and various maps relating to the American Civil War. Bien also issued several atlases both privately and in conjunction with a relation, Joseph Bien. At the height of his career Bien was elected president of the American Lithographers Association. After his death in 1909, Bien's firm was taken over by his son who promptly ran it into insolvency. The firm was sold to Sheldon Franklin, who, as part of the deal, retained the right to publish under the Julius Bien imprint. In addition to his work as a printer, Bien was active in the New York German Jewish community. He was director of the New York Hebrew Technical Institute, the New York Hebrew Orphan Asylum, and president of the B'nai B'rith Order. Learn More...