This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
1724 De L'Isle Map of Persia (Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan)
Persia-delisle-1724
Title
1724 (undated) 20 x 25 in (50.8 x 63.5 cm)
Description
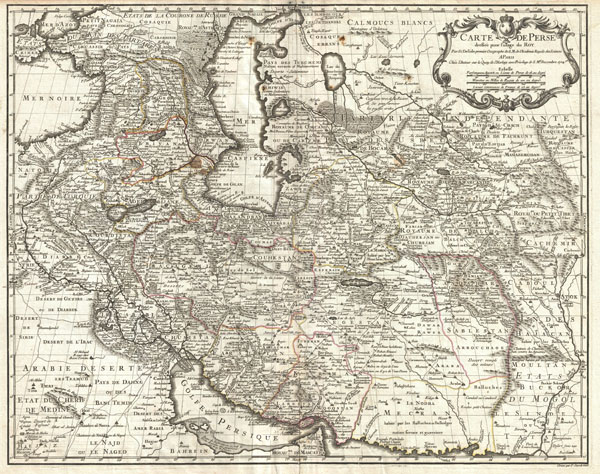
Cartographically De L'Isle's mapping of Persia marks a significant advance in European cartographic knowledge of the region. This map benefits considerably from Russian cartographic surveys and other sources no doubt smuggled to Guillaume De L'Isle by his brother Nicholas de L'Isle, who held a cartographic position with the Russian Academy of Sciences. The extent to which Russian data influenced this map is nowhere more evident than in De L'Isle's remarkable rendering of the Caspian Sea – one of the first accurate maps of the great lake to follow Van Verden's historic survey of 1721. Russian cartographic information is also apparent with regard to place names, such as the Russian name for the Aral Sea (Glouchoiye). It is equally likely that De L'Isle drew on Russian sources for his mapping of the Silk Route centers of Bukhara, Samarkand, and Ferghana, which were known stopping points for Russian trade envoys to China.
For the remainder of Persia De L'Isle most likely updated Persian and Arabic cartographic information with reports from Georgian and Armenian traders and mercenaries active throughout Persia. It may be through these sources that De L'Isle was able to add considerable geographic information regarding trade routes and place names in central Persia. These include such significant advances as the identification of Terheran (Tiheran), the current capital of Iran, which is notable absent it earlier European maps of Persia.
This map was drawn by Guillaume De L'Isle and engraved by P. Starckman. It issued independently as well as included in a number of composite atlases including De L'Isle's 1731 Atlas de Geographie. A number of reissues by Buache, Covens & Mortier, and others followed.
Cartographer
The De L'Isle family (fl. c. 1700 - c. 1760) (also written Delisle) were, in composite, a mapmaking tour de force who redefined early 18th century European cartography. Claude De L'Isle (1644 -1720), the family patriarch, was Paris based a historian and geographer under Nicholas Sanson. De L'Isle and his sons were proponents of the school of "positive geography" and were definitive figures, defining the heights of the Golden Age of French Cartography. Of his twelve sons, four, Guillaume (1675 - 1726), Simon Claude (1675 - 1726), Joseph Nicholas (1688 - 1768) and Louis (1720 - 1745), made a significant contributions to cartography. Without a doubt Guillaume was the most remarkable member of the family. It is said that Guillaume's skill as a cartographer was so prodigious that he drew his first map at just nine years of age. He was tutored by J. D. Cassini in astronomy, science, mathematics and cartography. By applying these diverse disciplines to the vast stores of information provided by 18th century navigators, Guillaume created the technique that came to be known as "scientific cartography", essentially an extension of Sanson's "positive geography". This revolutionary approach transformed the field of cartography and created a more accurate picture of the world. Among Guillaume's many firsts are the first naming of Texas, the first correct map of the Mississippi, the final rejection of the insular California fallacy, and the first identification of the correct longitudes of America. Stylistically De L'Isle also initiated important changes to the medium, eschewing the flamboyant Dutch style of the previous century in favor of a highly detailed yet still decorative approach that yielded map both beautiful and informative. Guillaume was elected to the French Academie Royale des Sciences at 27. Later, in 1718, he was also appointed "Premier Geographe du Roi", an office created especially for him. De L'Isle personally financed the publication of most of his maps, hoping to make heavy royalties on their sales. Unfortunately he met an untimely death in 1728, leaving considerable debt and an impoverished child and widow. De L'Isle's publishing firm was taken over by his assistant, Phillipe Buache who became, posthumously, his son in law. The other De L'Isle brothers, Joseph Nicholas and Louis De L'Isle, were employed in the Service of Peter the Great of Russia as astronomers and surveyors. They are responsible for cataloguing and compiling the data obtained from Russian expeditions in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America, including the seminal explorations of Vitus Bering and Aleksei Chirikov. The De L'Isles, like their rivals the Vaugondys , must be considered speculative geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown areas on their maps with speculations based upon their vast knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers and navigators. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered many rivalries. The era of speculatively cartography effectively ended with the late 18th century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. More by this mapmaker...