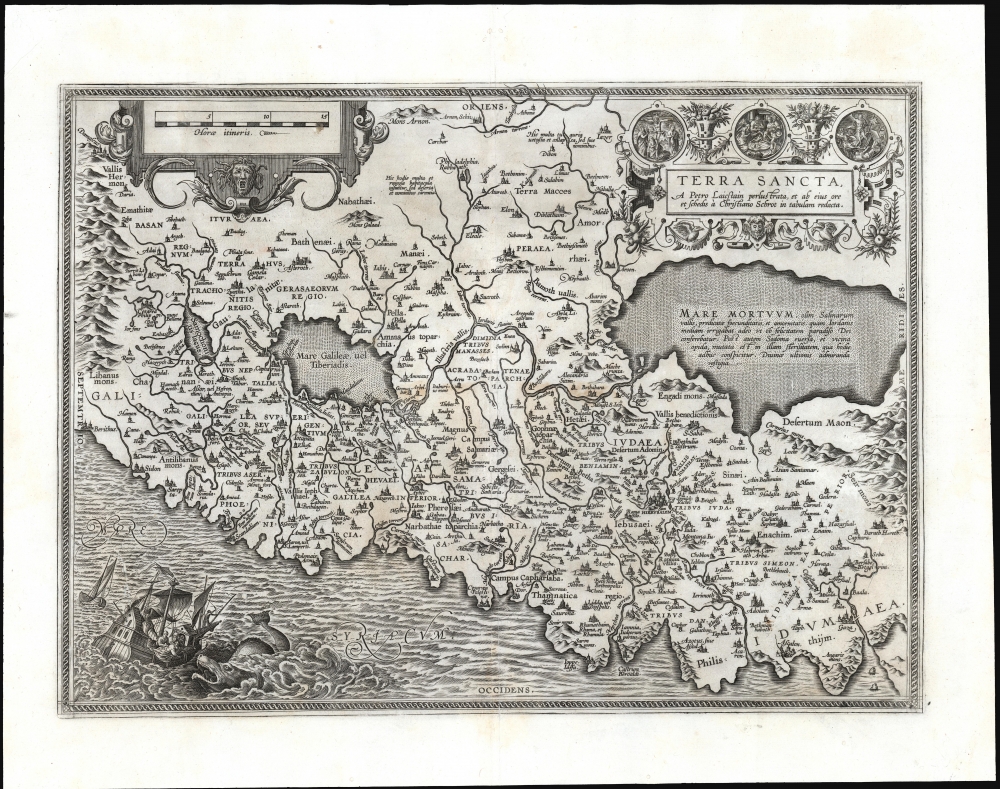
1584 Ortelius Map of the Holy Land / Israel / Palestine
HolyLand-ortelius-1584
Title
1584 (undated) 14.5 x 20 in (36.83 x 50.8 cm) 1 : 660000
Description
Scope of the Map
This eastern-oriented map traces the coastline from Beirut and the mountains of Lebanon to Gaza and the Seir mountains. It reaches as far east as the Wadi el-Mujib, here marked as Arnon Torrens (Biblically, the geographical separation of Moab from the tribes of Reuben and Gad). The map features a prominent Dead Sea and a Sea of Galilee. Mountains are indicated pictorially. Cities and regional names are predominantly Biblical, naming the Tribes of Judaea.The Sources
Ortelius' immediate source was a now-unobtainable 1570 nine-sheet map drawn by Christian Sgrooten. This work itself was drawn from the report by the Dutch astronomer Petrus Laiksteen, of his 1556 visit to the Holy Land (Sgrooten's map is the sole surviving evidence of this visit). So while the map is - typically of early maps of the Holy Land - primarily focused on the region as a Biblical location, its delineation and the placement of its features is unique among contemporaneous maps in being based on actual experience. This is revealed sharply in its notations describing ruined and nameless villages, doubtless actual descriptions of observations, nestled among the Biblical placenames.Publication History and Census
This map was engraved for inclusion in the 1584 edition of Abraham Ortelius' Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. There are two recorded states of the map, of which this is the second, identifiable by the further hachure and stippling added in 1595. The present example corresponds typographically to the 1598 French-text edition of the Theatrum. We see one example of this edition listed in OCLC, although the map in its various editions is well represented in institutional collections and appears on the market.Cartographer
Abraham Ortelius (April 14, 1527 - June 28, 1598) also known as Ortels, was a cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer of Brabant, active in Antwerp. He was the creator of the first modern atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum and is a seminal figure in the history of cartography. Along with Gerard Mercator and Gemma Frisius, he was a founder of the Netherlandish school of cartography. His connections with Spain - culminating in his 1575 appointment as Royal Cartographer to King Phillip II of Spain - gave him unmatched access to Spanish geographical knowledge during a crucial period of the Age of Discovery. Ortelius was born in 1527 in Antwerp. In 1547 he entered the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as an illuminator of maps. He began trading in books, prints, and maps, traveling regularly to the Frankfurt book and print fair, where in 1554 he met Mercator. He accompanied Mercator on journeys throughout France in 1560 and it was at this time, under Mercator's influence, that he appears to have chosen his career as a scientific geographer. His first published geographic work appeared in 1564, an eight-sheet cordiform world map. A handful of other maps preceded the 1570 publication of the first edition of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, which would prove to be his life work. Appearing with but 53 maps in its first edition, Ortelius' work expanded with new maps added regularly. By 1592, it had 134 maps. Many of Ortelius' maps remained the standard for nearly a century. He traveled extensively, but his genius was as a compiler, locating the best informed maps on which to base his own. His contacts throughout Europe and extending even (via the Portuguese) to the Far East were formidable. Moreover, many of his maps were based on his own scholarship, particularly his historical works. His theories of geography were particularly ahead of his time with respect to the notion of continental drift, the possibility of which he mused on as early as 1596, and which would be proven correct centuries later.
In a sense his greatest achievement was his successful navigation of the religious and political violence endemic to his city throughout his adult life: The Dutch Revolt, or Eighty Years' War (1568 - 1648), fully embroiled Antwerp. Although outwardly and officially recognized as Catholic (Arias Montanus vouched for Ortelius' Catholic orthodoxy prior to his appointment as Royal Geographer), Ortelius was able to separate himself from the religious furor which characterized the war in the low countries. Ortelius showed a glimpse of himself in a letter to a friend, regarding humanist Justus Lipsius: 'I do not know whether he is an adherent of the Pope or a Calvinist, but if he has ears to hear, he will neither be one nor the other, for sins are committed on both sides'. Ortelius' own explorations of Biblical history in his maps, and the Christogram contained in his own motto, suggest him to be a religious man, but his abjuration of political religious authorities mark him as an individualist. His tombstone at St Michael's Præmonstratensian Abbey in Antwerp bears the inscription, Quietis cultor sine lite, uxore, prole. ('served quietly, without accusation, wife, and offspring.') More by this mapmaker...