1758 Bellin Map of Barbados
Barbados-bellin-1758
Title
1758 (undated) 9.75 x 7.75 in (24.765 x 19.685 cm) 1 : 270000
Description
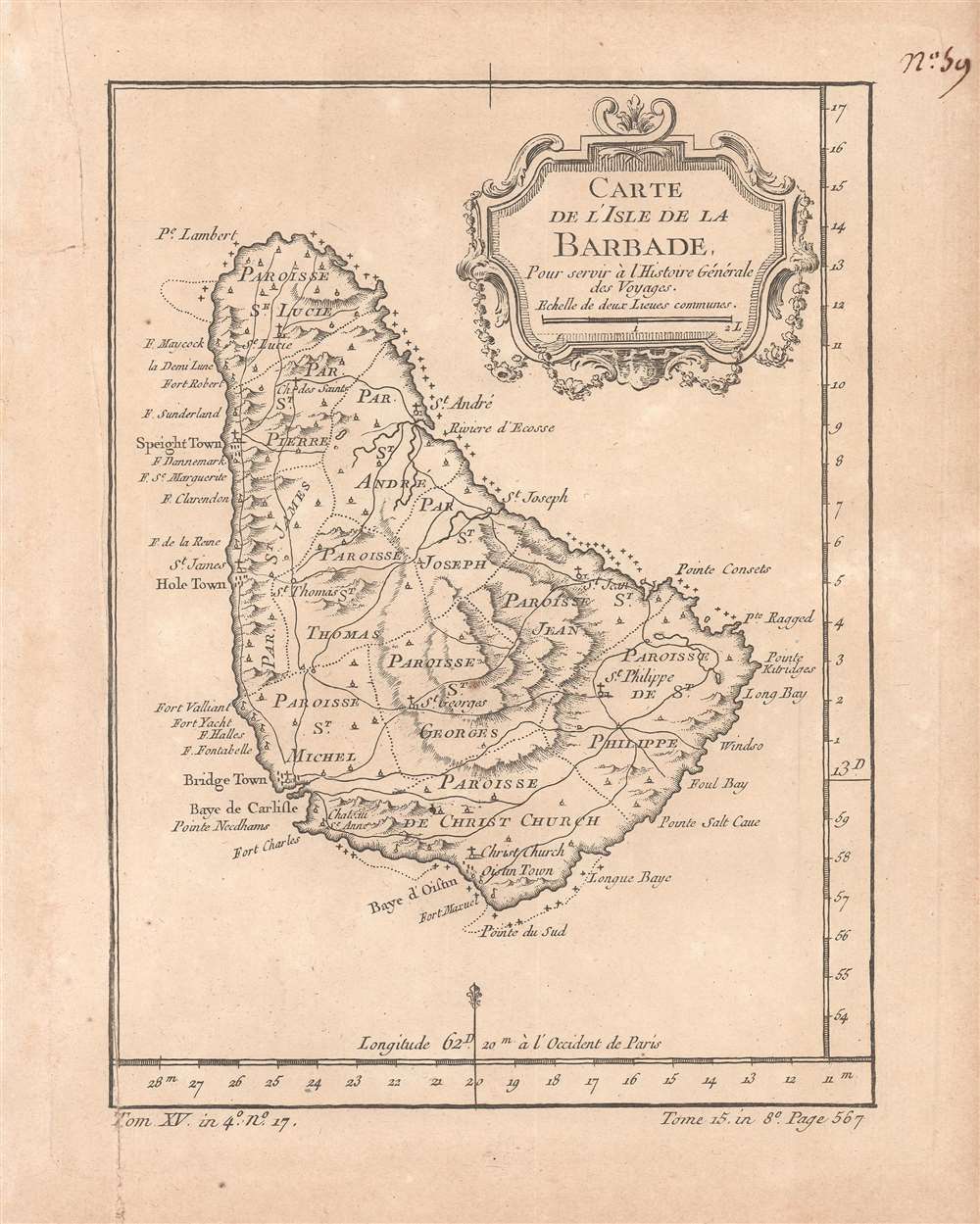
A Closer Look
The map takes in the entirety of Barbados, showing areas of elevation, the names and borders of parishes, towns (including the capital of Bridgetown in the island's southwest), roads, areas of cultivation, the location of churches, and coastal nautical indicators. As was standard for French maps of the time, longitude is measured in degrees from Paris rather than Greenwich.Historical Context
The history of Barbados is in many ways typical of the Caribbean, with disease and slave-raiding drastically reducing the indigenous population soon after contact. In 1625, the English beca,e the first Europeans to settle permanently on Barbados. Soon afterwards, sugar cane was introduced from Dutch Brazil, and though Barbados was an English colony, Dutch plantation managers (many of whom were in fact descendants of Sephardic Jews expelled from Iberia) directed the plantation economy. Slave laborers were brought in from Africa in increasing numbers and nearly the entire island was switched over to a brutal system of sugar production, whereby absentee landlords living in England consolidated lands into a shrinking number of large plantations overseen by hired managers.In the mid-17th century, Barbados quickly replaced Hispaniola as the largest sugar-producing colony in the Caribbean and became the most profitable English colony in the Americas by a wide margin. In 1661, the Parliament of Barbados passed the Barbados Slave Code, the first such Slave Act, which became a model throughout the Americas. Though ostensibly meant to prevent especially cruel treatment of slaves, such as wanton killing, the Barbados Slave Code and its imitators codified the status of slaves as chattel property and permitted a range of incredibly brutal reprisals for acts of disobedience.
As with the British Empire as a whole, the slave trade was outlawed in Barbados in 1807 but the institution of slavery continued for nearly thirty years afterwards. The intervening years were tense and uncertain, as public opinion and the law were clearly moving towards emancipation, but only at a snail's pace. In April 1816, a large slave rebellion broke out in Barbados, led by an African-born man named Bussa. The rebels seem to have caught wind of debates over abolition in Britain and were distraught at the slow pace of progress. The revolt failed, but, along with uprisings in Guyana and Jamaica, likely accelerated the pace of abolition. Bussa is still honored as a national hero and a large statue dedicated to him was built in the capital, Bridgetown, in 1985. Barbados became independent in 1966 and joined the Commonwealth of Nations. On New Year's Day, 2022, Barbados severed ties with the British monarchy and became a republic, though it remains in the British Commonwealth.
Publication History and Census
This map was first printed in 1752 to accompany the Abbé Antoine François Prévost's Histoire générale des voyages and then reprinted several times thereafter, often elaborated with coloring. This is likely an early edition, given its relatively simple presentation and small size, as opposed to larger print sizes in later editions. The present edition is held by the University of Michigan and the University of Florida and is scarce to the market.CartographerS
Jacques-Nicolas Bellin (1703 - March 21, 1772) was one of the most important cartographers of the 18th century. With a career spanning some 50 years, Bellin is best understood as geographe de cabinet and transitional mapmaker spanning the gap between 18th and early-19th century cartographic styles. His long career as Hydrographer and Ingénieur Hydrographe at the French Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine resulted in hundreds of high quality nautical charts of practically everywhere in the world. A true child of the Enlightenment Era, Bellin's work focuses on function and accuracy tending in the process to be less decorative than the earlier 17th and 18th century cartographic work. Unlike many of his contemporaries, Bellin was always careful to cite his references and his scholarly corpus consists of over 1400 articles on geography prepared for Diderot's Encyclopedie. Bellin, despite his extraordinary success, may not have enjoyed his work, which is described as "long, unpleasant, and hard." In addition to numerous maps and charts published during his lifetime, many of Bellin's maps were updated (or not) and published posthumously. He was succeeded as Ingénieur Hydrographe by his student, also a prolific and influential cartographer, Rigobert Bonne. More by this mapmaker...
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles (April 1, 1697 – November 25, 1763), usually known the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. Having had difficulty in his youth determining a preference for life in the military or life among the Jesuits, he eventually wound up with the Benedictines, with whom he took vows. Despite his taking the vows, the vows evidently did not take with him: in 1728 he abandoned his abbey and fled to London. Naturally, he became a writer. In this he was prolific, both producing his own work and translations of others. Beginning in 1726, he published the first volume of his Histoire générale des voyages, which he worked on for the remained of his life and which was completed by his associates after his death, stretching to 25 volumes. Learn More...