This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
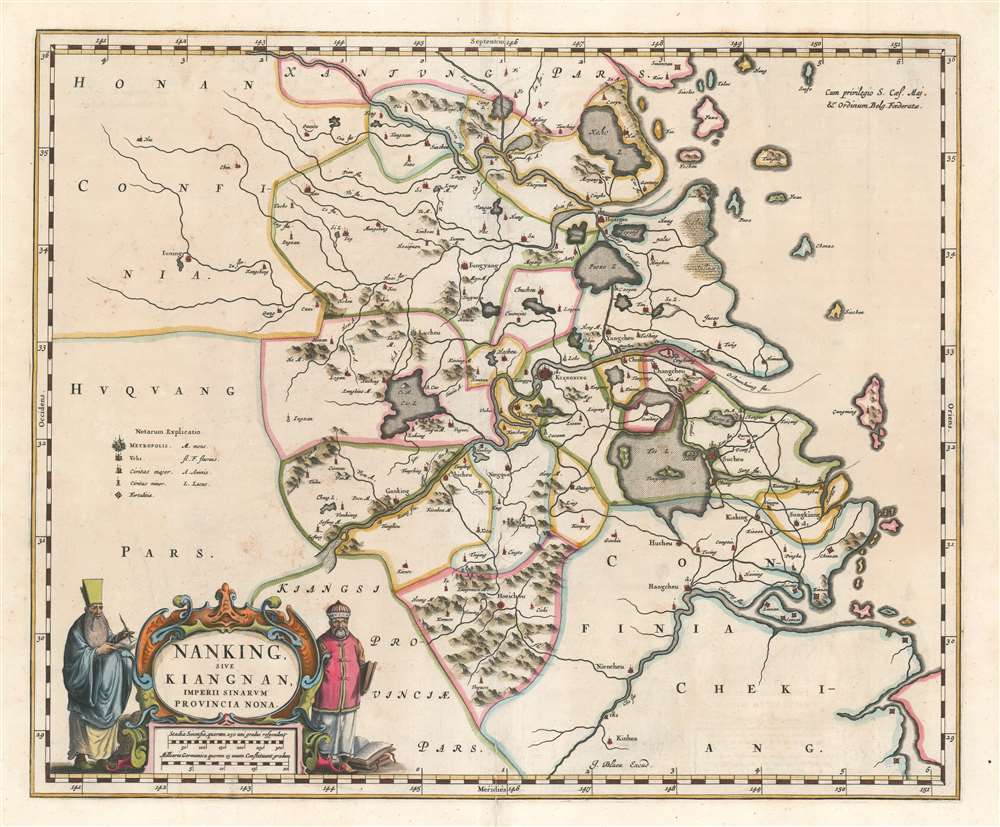
1662 Blaeu Map of Jiangsu Province and Shanghai Municipality, China
Nanking-blaeu-1662
Title
1662 (undated) 16.75 x 20.5 in (42.545 x 52.07 cm) 1 : 2200000
Description
One of the Four Ancient Capitals of China, Nanjing served as the capital of the Wu Kingdom during the Three Kingdoms Period in 229 A.D. Then, during the Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644), Nanjing served as one of the Chinese Empire's two capitals and was one of the most populous cities in the world. After the fall of Beijing to the Qing Emperor Li Zicheng in June 1644, Nanjing became the capital of the so-called Southern Ming Dynasty following the enthronement the Ming Prince Zhu Yousong. The Southern Ming Dynasty would survive and rule ever diminishing territory until the 1660s, when it was finally conquered by the Manchus.
This map was created by Joan Blaeu from work undertaken by the Jesuit missionary Martino Martini and published c. 1662. This map is a must-have for anyone interested in material relating to Shanghai.
CartographerS
Martino Martini (September 20, 1614 - June 6, 1661) was an Italian Jesuit missionary, historian, and cartographer, working mainly on ancient Imperial China. He is acclaimed as the father of Chinese geographical science, as he was ‘the first to study the history and geography of China with rigorous scientific objectivity.' Born in Trento, in the Bishopric of Trent, he finished school in 1631. After, he entered the Society of Jesus and was sent to study classical letters and philosophy at the Roman College, Rome, from 1634 until 1637. He completed his theological studies in Portugal from 1637 until 1639 and was ordained as a priest in Lisbon in 1639. He left for China in 1640, arriving in 1642 in Portuguese Macau. He studied Chinese before, in 1642, moving to Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province. He spent much of his time traveling and gathering scientific information, particularly concerning the geography. In April 1644, soon after his arrival in China, the Ming capital Beijing fell to Li Zicheng’s rebels and then to the Manchus. Martini had been allied with the short-lived regime of Zhu Yujian, Prince of Tang, who declared himself the (Southern) Ming Longwu Emperor after the fall of the last legitimate Ming, the Chongzhen Emperor. When Wenzhou, where Martini was on a mission for Zhu Yujian, was about to fall to the Manchus, Martini convinced them to allow him to change sides. Before the Manchu troops entered the city, Martini created a large red poster stating, 'Here lives a doctor of the divine Law who has come from the Great West.' Below the poster he arranged tables with European books, astronomical instruments, and other objects surrounding an altar with an image of Jesus. The commander of the Manchu troops was so impressed by the display that he politely asked Martini to change sides. In 1651, Martini left China as the Delegate of the Chinese Mission Superior. Among the works he brought with him was Lo Hongxian's (羅洪先; 1504 - 1564) 1555 revision of Zhu Siben's (朱思本;1273 - 1333) 1312 manuscript atlas of the Chinese Provinces, Guang Yu Tu (廣與圖; 'Enlarged Territorial Atlas'). En route, his ship was captured by the Dutch, who apparently also saw Martini's value: they took him first to Java, and then to Amsterdam, where he arrived in 1654. During this intervening period, Martini translated the Zhu Siben atlas into Latin, and added his own description of China. The Blaeu mapmaking firm swiftly published Martini's map as Novus Atlas Sinensis, and later published Martini's description of China both on its own and within the Blaeu Atlas. After his circuitous journey, he reached Rome in the spring of 1655. He carried with him a long and detailed communication from the Jesuit missionaries in China, defending the so-called Chinese Rights (veneration of ancestors and other practices allowed to new Christians). After five months of discussions and debates, the Propaganda Fide issued a degree in favor of the Jesuits, although the controversy did not abate. More by this mapmaker...
Joan (Johannes) Blaeu (September 23, 1596 - December 21, 1673) was a Dutch cartographer active in the 17th century. Joan was the son of Willem Janszoon Blaeu, founder of the Blaeu firm. Like his father Willem, Johannes was born in Alkmaar, North Holland. He studied Law, attaining a doctorate, before moving to Amsterdam to join the family mapmaking business. In 1633, Willem arranged for Johannes to take over Hessel Gerritsz's position as the official chartmaker of the Dutch East India Company, although little is known of his work for that organization, which was by contract and oath secretive. What is known is his work supplying the fabulously wealthy VOC with charts was exceedingly profitable. Where other cartographers often fell into financial ruin, the Blaeu firm thrived. It was most likely those profits that allowed the firm to publish the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, sive, Atlas Novus, their most significant and best-known publication. When Willem Blaeu died in 1638, Johannes, along with his brother Cornelius Blaeu (1616 - 1648) took over the management of the Blaeu firm. In 1662, Joan and Cornelius produced a vastly expanded and updated work, the Atlas Maior, whose handful of editions ranged from 9 to an astonishing 12 volumes. Under the brothers' capable management, the firm continued to prosper until the 1672 Great Amsterdam Fire destroyed their offices and most of their printing plates. Johannes Blaeu, witnessing the destruction of his life's work, died in despondence the following year. He is buried in the Dutch Reformist cemetery of Westerkerk. Johannes Blaeu was survived by his son, also Johannes but commonly called Joan II, who inherited the family's VOC contract, for whom he compiled maps until 1712. Learn More...