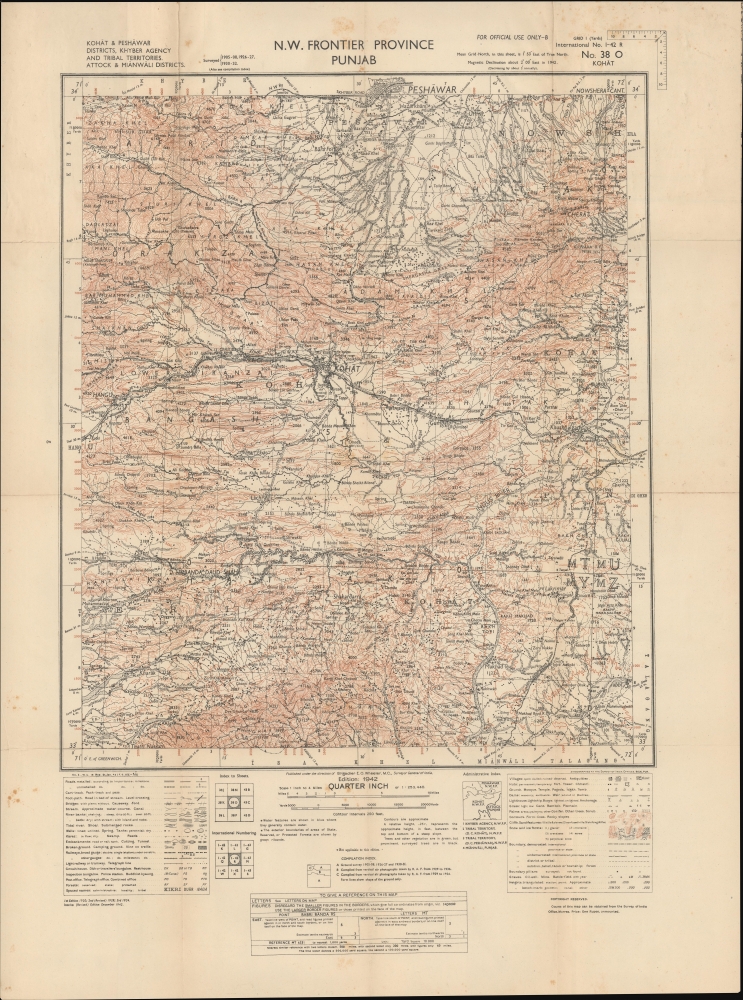
1942 Survey of India Map of North-West Frontier Province, Punjab
Punjab-surveyofindia-1942
Title
1942 (dated) 26.25 x 19.5 in (66.675 x 49.53 cm) 1 : 253440
Description
A Closer Look
Covering from Peshawar at top to Karak (Kharak) at bottom and east across the Indus River towards Rawalpindi, this map covers an area spanning parts of the North-West Frontier Province and Punjab Province of British India (now Pakistan). Peshawar is prominent along the top border, while Kohat predominates near center. The Indus River cuts diagonally across the map towards bottom-right. Among the incredible variety of features denoted by symbols in the legend at bottom-left, railways and roads are particularly important, especially the North-West (State) Railway and North-West Frontier roads, which allowed the British, with great difficulty, to attempt to assert control over the frontier in the mid-late 19th century. Special attention is also given to topography, terrain, and water sources, all of which would be important in the course of a military campaign.Guarding the Frontier
Though mostly based on earlier surveys, this map was produced during the Second World War. There was little immediate risk of the area being invaded by the Japanese, but there was nevertheless a significant British military presence there. Around Kohat are air firing and air bombing ranges, established in the 1920s to train pilots. Initially, these pilots were expected to be prepared to fight against tribesmen further to the north and west who never fully accepted British control. But during the World War II, the facilities were used to train and rotate airmen from the Burma Front. As for ground forces, this area was garrisoned, as had been the case since the 1850s, by units largely consisting of Sikhs (formerly the Punjab Irregular Force, by this time divided into the 12th Frontier Force Regiment and the 13th Frontier Force Rifles).Wartime Independence Movement
In addition to conflict on the frontier, the war years were highly tumultuous as Indian independence sentiment reached new heights. The same year this map was produced, the Quit India Movement was launched, resulting in the near-immediate arrest of Mahatma Gandhi and tens of thousands of other independence activists. The Punjab spawned a large number of leading independence fighters from across different religious communities.Zincography
Zincography, or 'zinco' for short, is a planographic printing process similar to lithography. The process was known as early as 1801, when lithography inventor Alois Senefelder (1771 - 1834), in his original English patent for lithography, mentioned the possibility of using zinc plates over traditional limestone. The first zincographic process was subsequently patented in 1834 by Federico Lacelli. The process operates like traditional stone-lithography wherein ink applied to the plate is repelled by the hygroscopic areas, and attracted to the fuchsine areas. It offers several advantages, most importantly, zinc plates are lighter and cheaper than lithographic stones, economizing the process considerably. As such, the process was embraced by various cartographic agencies that demanded mobility and economy, among them the British Ordinance Survey, the French Bureau Topographique, and many military mapping agencies. It was followed by photo-zincography, photo-lithography, and photogravure.Publication History and Census
This map was produced by the Survey of India in 1942, based on a map first printed in 1920 but relying on surveys dating back to 1905. Nevertheless, the present map differs considerably from earlier editions, adding a bewildering amount of detail. The only known example of this map in institutional collections is held by the University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee's American Geographical Society Library. The Survey of India also produced a 1941 map of the same region, but on a scale of one inch to one mile (OCLC 1277312015, 1277297658), only held by the Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale di Roma.Cartographer
Survey of India (1767 - Present) is India's central engineering agency in charge of mapping and surveying the country. It was founded in 1767 by Major James Rennell, who took the post of first Surveyor General, with the mission to map and consolidate the territories of the British East India Company. The Survey undertook the Great Trigonometrical Survey between 1802 and 1852 in an attempt to accurately measure the Indian Subcontinent - considered one of the greatest feats of mapping of all time. It also sponsored clandestine surveys, at times disguised as Buddhist pilgrims, to infiltrate and map Tibet, then a closed country. With India's independence in 1947, the Survey was folded into the new Indian government, which it remains part of to this day. More by this mapmaker...