This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
1896 Rand McNally Wall Map of the United States w/ Union Pacific Railroad
UnionPacificUnitedStates-randmcnally-1896
Title
1887 (undated) 36 x 55 in (91.44 x 139.7 cm) 1 : 3580000
Description
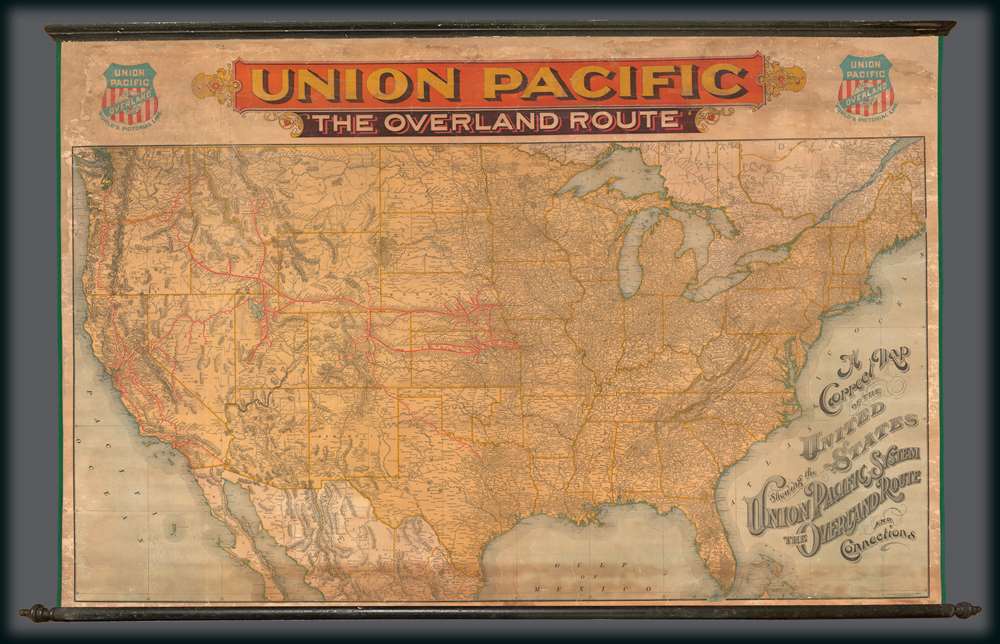
The Union Pacific: The Overland Route
The Union Pacific Rail Road was founded in July of 1862, in the midst of the American Civil War. It was constructed in two parts, westward from Council Bluffs, Iowa to meet the Central Pacific Railroad line, which was constructed eastward from Sacramento, California. The Golden Spike was driven by railroad tycoon Leland Stanford at Promontory Summit, Utah Territory on May 10, 1869, connecting the lines and creating first transcontinental railroad. Combined, the Union Pacific-Central Pacific Railway line became known as the 'Overland Route.' Nonetheless, by 1896, the Union Pacific was no longer the only fully linked line leading westward, as both the Northern Pacific and the Southern Pacific were in operation, and to the credit of the mapmakers both appear, if in de-emphasized forms. Even so, none of the competing routes offered the size and flexibility of the Union Pacific. By the early 20the century the Union Pacific had absorbed most competing lines and is today one of the world's largest railroad concerns.Publication History and Census
The map was published by the Rand McNally Company in Chicago on behalf o the Union Pacific Railroad. It is rare and likely issued in small quantities for use only in large railway stations. We have been able to isolate examples at the University of Kentucky and at the Denver Public Library. There appears to be but one edition.CartographerS
Rand, McNally and Co. (fl. 1856 - present) is an American publisher of maps, atlases and globes. The company was founded in 1856 when William H. Rand, a native of Quincy, Massachusetts, opened a print shop in Chicago. Rand hired the recent Irish immigrant Andrew McNally to assist in the shop giving him a wage of 9 USD per week. The duo landed several important contracts, including the Tribune's (later renamed the Chicago Tribune) printing operation. In 1872, Rand McNally produced its first map, a railroad guide, using a new cost effective printing technique known as wax process engraving. As Chicago developed as a railway hub, the Rand firm, now incorporated as Rand McNally, began producing a wide array of railroad maps and guides. Over time, the firm expanded into atlases, globes, educational material, and general literature. By embracing the wax engraving process, Rand McNally was able to dominate the map and atlas market, pushing more traditional American lithographic publishers like Colton, Johnson, and Mitchell out of business. Eventually Rand McNally opened an annex office in New York City headed by Caleb S. Hammond, whose name is today synonymous with maps and atlases, and who later started his own map company, C. S. Hammond & Co. Both firms remain in business. More by this mapmaker...
Matthews-Northrup Works (fl. c. 1895 - 1930) were a Buffalo, New York based, in their own words, "writing, designing, engraving, printing, [and] binding" firm. The firm was founded by James Newson Matthews (November 21, 1828 - December 20, 1888) as the J. N. Matthews Company. William Phelps Northrup (April 2, 1850 - February 2, 1929) later joined the company as an apprentice and then partner, at which point the firm was reincorporated as the Matthews-Northrup Works. The Matthews-Northrup Works rose to prominence as publishers and printers of railroad maps, with dozens to their credit. When James died, his shares were inhered by George Edward Matthews (1855 - 1910), who ran the business until his death in 1910. Also in 1910, they famously redesigned the cover of National Geographic Magazine. Despite some six previous cover changes in just 21 years, the Matthews-Northrup layout proved so popular that it was used for nearly 50 years. The firm can also take credit for the Winchell typeface, designed in 1903 under E. E. Winchell's tenure as art director. Curiously, the partners of Matthews-Northrup maintained an unusual affectation in which only the officers of the company could wear beards or mustaches. In this same spirit, the firm also had its own private social club, the Fellowcraft Club, where the all-male employees could relax, play pool, drink and dine. Matthews-Northrup maintained offices on Washington Street, Buffalo, where they were based, as well as Madison Square, New York City, Garden Tower, Boston, and the Citizens Building in Cleveland. Learn More...