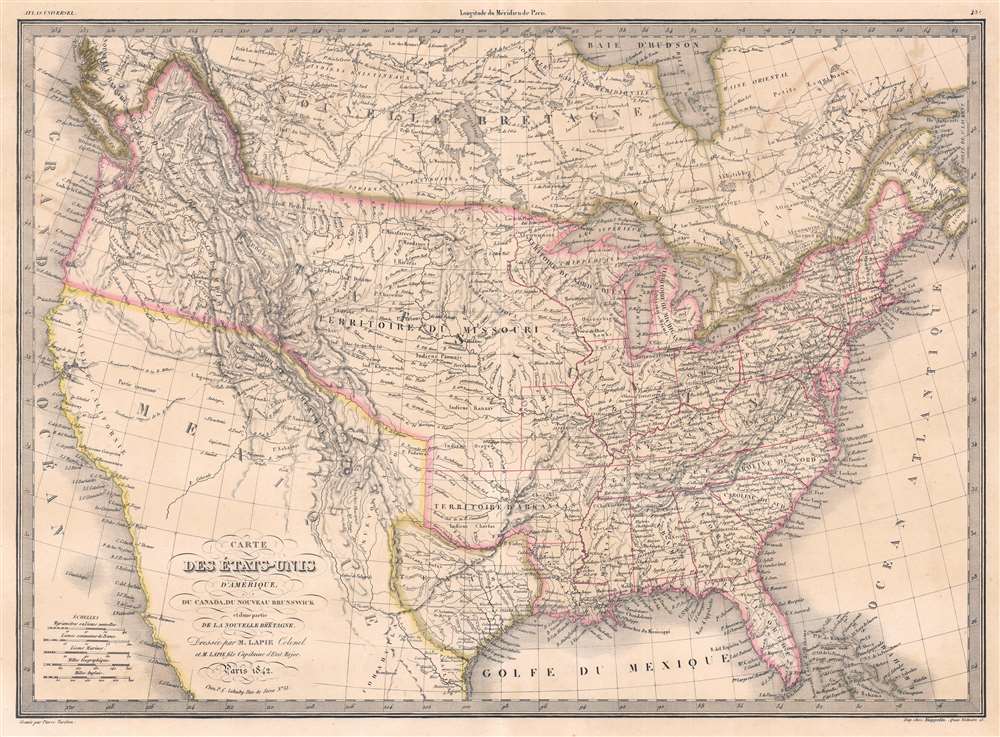
1842 Lapie Map of the United States with the Republic of Texas
UnitedStates-lapie-1842
Title
1842 (dated) 16.25 x 22 in (41.275 x 55.88 cm) 1 : 9300000
Description
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas was a short-lived nation established in March of 1836 when it ceded from Mexico. Following the independence of Mexico from Spain, the American Stephen Fuller Austin lead a group of 300 Empresarios to settle Texas, near Austin, where they received a grant from the Mexican government. As more Americans moved to Texas, resentment and strife began to build between the American settlers and Mexican authorities. This and other factors ultimately led to the Texan Revolution in 1835 and the declaration of Texan independence in 1836. Texas remained an independent republic until it joined the United States 10 years later in 1846.Texas Borders
The borders of the Republic of Texas were in dispute from the earliest days of the Texan Revolution. The Republic-claimed borders followed the Treaties of Velasco between the newly created Texas Republic and Mexican leader, Antonio López de Santa Anna. The treaties established an eastern boundary following the 1819 Adams-Onís Treaty between the United States and Spain, which established the Sabine River as the eastern boundary of Spanish Texas and western boundary of the Missouri Territory. The Republic's southern and western boundary with Mexico was more nuanced. Texas claimed the Rio Grande del Norte as its western and southernmost border, while Mexico argued for a boundary much further east at the Nueces River. When Texas was annexed into the United States, the agreement followed the Republic claimed boundary, thus absorbing Mexican claimed territory as far west as Santa Fe. This escalated already existing tensions between the United States, the former Republic of Texas, and Mexico, ultimately triggering for the Mexican-American War (1846 - 1848).France Recognizes the Republic of Texas
When Texas ceded from Mexico on April 21 of 1836, it immediately sought legitimacy through diplomatic appeals to major world powers - most of which were in Europe. Most European powers were reluctant to recognize the self-proclaimed Republic until it became clear that it could survive and what diplomatic ramifications, if any, formal recognition might yield. Nonetheless, France under King Louis Phliippe recognized Texas on September 25, 1839. This act may have been partially trade inspired, and partially motivated by French antipathy towards Mexico following the First French Intervention or Pastry War (1838 - 1839). Recognizing Texas diplomatically allowed France to open official trade channels, particularly for cotton, a vital commodity in Europe and an increasing cause of tension between France and Britain. Moreover, the recognition of Texas accelerated the destabilization of Mexico, increasing the probability that any colonial aspirations the French may have had in seizing California would be successful.The National Road
The National Road, begun in 1811 and completed in 1837, was the first major improved highway in the United States. The road, illustrated here by a thin black line, connected the Ohio and Potomac Rivers, and stretched from Cumberland, Maryland to Vandalia, Illinois, the Illinois state capital at the time. Construction of the road came to an end when federal funding dried up in the Panic of 1837.Columbia District
The Columbia District, situated in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, was a fur trading district originally explored by the North West Company beginning in 1793. The Hudson's Bay Company, the North West Company's main rival in the fur trade, and the North West Company violently competed for trapping rights in the region, which even escalated into a small war, known as the Pemmican War. To put an end to this nonsense, the British government forcibly merged the two companies in 1821. By this time, the Columbia District, or as it had become known the Columbia Department, overlapped significantly with the Oregon Territory claimed by the United States, which eventually led to a border dispute between British North America (Canada) and the U.S. A treaty signed in 1846 formally ended the border dispute and set the U.S.-British border at the 49th parallel.Publication History and Census
This map was created by Pierre and Alexandre Lapie and engraved by Pierre Tardieu for publication in the 1842 edition of their Atlas Universel de Géographie Ancienne et Moderne published by P.C. Lehuby. The 1842 edition of Lapie's map of the United States is well represented in institutional collections.CartographerS
Pierre M. Lapie (fl. 1779 - 1850) and his son Alexandre Emile Lapie (fl. 1809 - 1850) were French cartographers and engravers active in the early part of the 19th century. The Lapies were commissioned officers in the French army holding the ranks of Colonel and Capitan, respectively. Alexander enjoyed the title of "First Geographer to the King", and this title appears on several of his atlases. Both father and son were exceptional engravers and fastidious cartographers. Working separately and jointly they published four important atlases, an 1811 Atlas of the French Empire (Alexander), the 1812 Atlas Classique et Universel (Pierre), the Atlas Universel de Geographie Ancienne et Modern (joint issue), and the 1848 Atlas Militaire (Alexander). They also issued many smaller maps and independent issues. All of these are products of exceptional beauty and detail. Despite producing many beautiful maps and atlases, the work of the Lapie family remains largely underappreciated by most modern collectors and map historians. The later 19th century cartographer A. H. Dufour claimed to be a student of Lapie, though it is unclear if he was referring to the father or the son. The work of the Lapie firm, with its precise engraving and informational density, strongly influenced the mid-19th century German commercial map publishers whose maps would eventually dominate the continental market. More by this mapmaker...
Pierre-Alexandre Tardieu (March 2, 1756 - August 3, 1844) was a French portrait and historical engraver of the large Paris-based Tardieu family. The Tardieu family was extremely prolific, with numerous members, for over 200 years, being skilled and active engravers. Most of the Tardieu engravers simply identified themselves as 'Tardieu' or at best with their initials, so it is often extremely difficult to distinguish their individual work. Pierre-Alexandre Tardieu was the son of Pierre-Joseph Tardieu. Pierre-Alexandre was the last of the great masters of the engraving school of the 17th and 18th centuries. He worked for nearly seventy years, and was heralded for the diversity of his works. He was originally a student of his uncle Jacques-Nicolas Tardieu. Learn More...