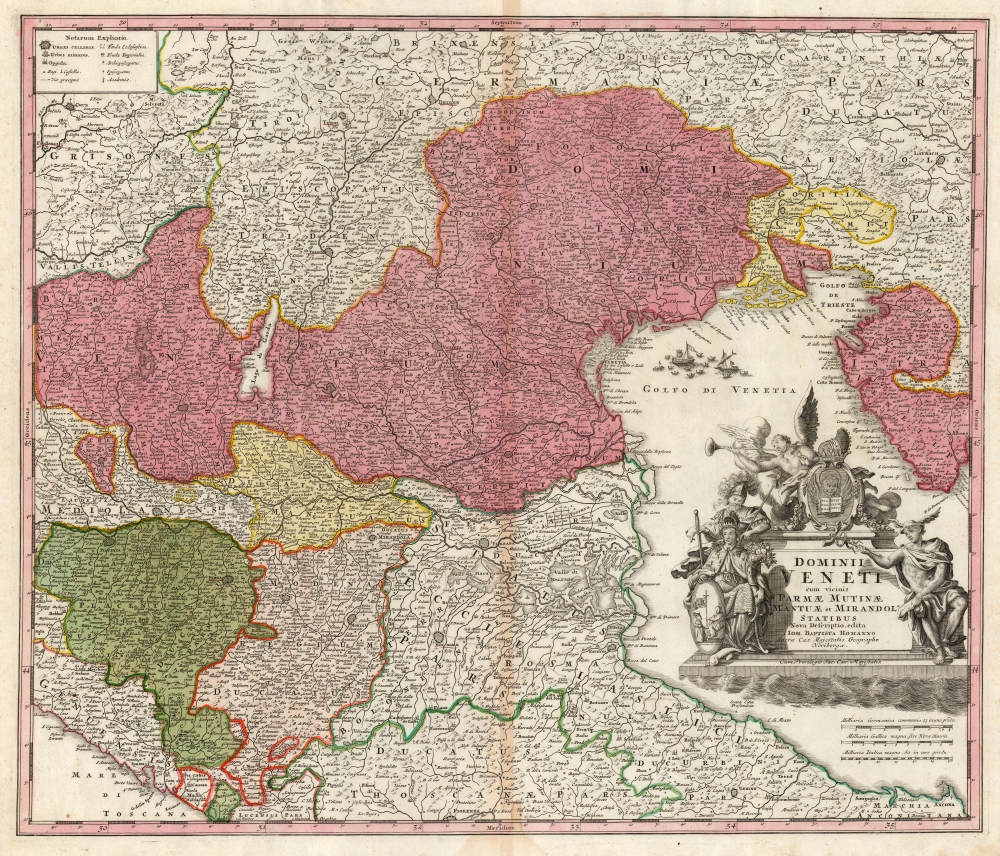
1730 Homann Map of the Republic of Venice
VeniceRepublic-homann-1716
Title
1716 (undated) 19 x 22.5 in (48.26 x 57.15 cm) 1 : 815000
Description
Scope
The map spans from the Duchy of Parma and Piacenza in the west to Croatia in the east and from the Tyrol in the north to part of Tuscany in the south - Florence appears at the southern limit. The map's detail extends to towns, rivers, lakes, cities, and topographical features. For example, the region between Ferrara and Ravenna focusing on the lagoon of the Valle di Comacchio is painstakingly presented.The Source
Homann's map is closely copied from the De Wit map of c. 1701, with the exception that it does not include the details specific to the first moves of the War of Spanish Succession (1701 - 1714), which had ended by the time this map was produced, and from which Venice had remained neutral.The Cartouche
Seated at the left is the Doge of Venice. He has under his arm a cornucopia, both a symbol of plenty and possibly a play on the name of the Doge's family name, Cornaro. Ares, the god of war, looks down protectively. On the other flank of the cartouche, Hermes - the messenger of the gods, and patron of commerce - gestures with his caduceus. Atop the cartouche behind the Venetian arms, winged Fame blows her horn, holding a ring in her other hand - a symbol which may allude to eternity. Unintentionally ironic, in that Venice had already begun her decline as a sea power and would, by the end of the century, be unable to defend herself from the threat of Napoleon.Publication History and Census
This map was initially engraved for publication in Homann's 1716 Atlas Novus Terrarum Orbis Imperia, Regna Et Status exactis Tabulis Geographicè demonstrans. The present example's inclusion of the Imperial privilege suggests that it dates to about 1730. The map undergoes many state changes. Between different editions, we see enough reworking to the cartouche to suggest that there may even be more than one plate of the map. There is, unfortunately, no thorough census tracing these alterations, and OCLC is seldom precise in its dating for this work. In its various issues, the map is nevertheless well represented in institutional collections.CartographerS
Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man, Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest. Nonetheless, he converted to Protestantism in 1687, when he was 23. It is not clear where he mastered engraving, but we believe it may have been in Amsterdam. Homann's earliest work we have identified is about 1689, and already exhibits a high degree of mastery. Around 1691, Homann moved to Nuremberg and registered as a notary. By this time, he was already making maps, and very good ones at that. He produced a map of the environs of Nürnberg in 1691/92, which suggests he was already a master engraver. Around 1693, Homann briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Until 1702, he worked in Nuremberg in the map trade under Jacob von Sandrart (1630 - 1708) and then David Funck (1642 - 1709). Afterward, he returned to Nuremberg, where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years, Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy, detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. Due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, the Homann firm could undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching their diversity and quality. Despite copious output, Homann did not release his first major atlas until the 33-map Neuer Atlas of 1707, followed by a 60-map edition of 1710. By 1715, Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year, he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with several significant advantages, including access to the most up-to-date cartographic information as well as the 'Privilege'. The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to very few by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though less sophisticated than modern copyright legislation, the Privilege offered limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription 'Cum Priviligio' or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1724, the firm's map plates and management passed to his son, Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger (1695 - 1760) and Johann Michael Franz (1700 - 1761), and that it would publish only under the name 'Homann Heirs'. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc.) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever-diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo (1781 - 1848). More by this mapmaker...
Frederik de Wit (1629 - 1706) was a Dutch Golden Age cartographer active in the second half of the 17th and the early 18th centuries. De Wit was born of middle class Protestant stock in the western Netherlandish town of Gouda. He relocated to Amsterdam sometime before 1648, where he worked under Willem Blaeu. His first attributed engraved map, a plan of Haarlem for Antonius Sanderus' Flandria Illustrata, was issued around this time. He struck out on his own in 1654. The first chart that De Wit personally both drew and engraved was most likely his 1659 map of Denmark, REGNI DANIÆ Accuratissima delineatio Perfeckte Kaerte van ‘t CONJNCKRYCK DENEMARCKEN. His great wall map of the world and most famous work, Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula appeared one year later. Following the publication of his wall map De Wit quickly rose in prominence as a both cartographer and engraver. He married Maria van der Way in 1661 and through her became a citizen of Amsterdam in 1662. Around this time he also published his first major atlas, a composite production ranging in size from 17 to over 150 maps and charts. Other atlases and individual maps followed. In 1689 De Wit was granted a 15 year Privilege by the Dutch States General. (An early copyright that protected the recipient's rights to print and publish.) He was recognized with the honorific 'Good Citizen' in 1694. De Wit died in 1706 after which his wife Maria continued publishing his maps until about 1710. De Wit's son, Franciscus, had no interest in the map trade, instead choosing to prosper as a stockfish merchant. On her own retirement, Maria sold most De Wit maps and plates at a public auction. Most were acquired by Pieter Mortier and laid the groundwork for the 1721 rise of Covens and Mortier, the largest Dutch cartographic publishing house of the 18th century. Learn More...