This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
1656 Sanson Map of Canada and the Great Lakes
CanadaGreatLakes-sanson-1656
Title
1656 (dated) 16 x 21.5 in (40.64 x 54.61 cm) 1 : 9200000
Description
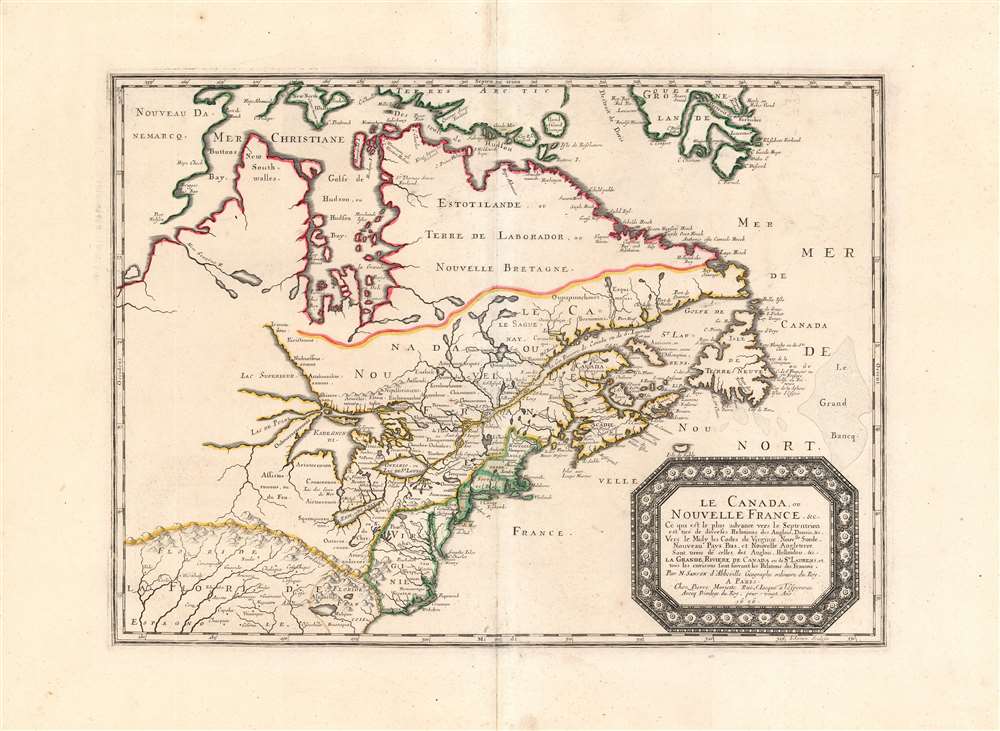
The map's treatment of the Arctic waters and Maritime Canada builds on Champlain's basic model, adding place names derived from Dutch and English exploration and preserving Button's explicit northwest passage leading from Button's Bay.
Five Great Lakes Shown and Named
Although Sanson's general map of North America was the first to depict all five Great Lakes recognizably, and the Boisseau was the first to name and show all five lakes at all, the present map reveals the Lakes and the St. Lawrence River in much finer detail. It was the first map of Canada to name Lake Erie. Lake Superior is named; Lake Huron carries the Wyandot name 'Karegnondi,' and Lake Michigan bears the name 'Lac de Puans,' which would later be applied to Green Bay.Indigenous Names Recorded
Beyond the names applied to the lakes, Sanson includes a wealth of indigenous place names. Although appearing in territories of New England as well, these are most numerous within the bounds of New France - where Sanson's Jesuit sources would have been best informed.Mapping the Colonial East Coast
The political borders of the map are distorted heavily in favor of the French, largely at the expense of the British colonies. In spite of this, the geographical delineation of the east coast is better detailed than French geography had yet produced. Sanson improves on his North America with the inclusion of Long Island, for example, and a more correct positioning of New Amsterdam. The Delaware River is also more accurately shown, including the short-lived colony of New Sweden. In spite of the French not having colonists there in almost a century, the region of the Carolinas is shown here as Floride Francois, relying on the early French Huguenot attempts to settle northern Florida to back the claim. The attempt was chronicled by Le Moyne in 1591. Within the boundaries of Floride Francois can be found two large inland lakes which first made their appearance on the De Bry / Le Moyne map of 1591, and which would appear on maps of the region throughout the 17th century. The larger of these is represented as the source of the River May, following the model of the Le Moyne. In the southwestern extreme of the map - amidst 'Floride Espagnole'- can be seen the upper portions of the imaginary network of rivers thought to empty into the Bahia del Spiritu Santo. Of the Mississippi River, nothing can yet be said to appear.Publication History and Census
This map was engraved by Jean Somer, Sanson's principle engraver, in 1656. It was issued separately until the publishing of Sanson's 1658 atlas, Les Cartes Generales de Toutes le Parties du Monde. Although the atlas appeared in many editions, the plate continued in use unchanged throughout the print history. Six examples of the atlas are catalogued in OCLC. The separate map is well represented in institutional collections.CartographerS
Nicolas Sanson (December 20, 1600 - July 7, 1667) and his descendants were the most influential French cartographers of the 17th century and laid the groundwork for the Golden Age of French Cartography. Sanson was born in Picardy, but his family was of Scottish Descent. He studied with the Jesuit Fathers at Amiens. Sanson started his career as a historian where, it is said, he turned to cartography as a way to illustrate his historical studies. In the course of his research some of his fine maps came to the attention of King Louis XIII who, admiring the quality of his work, appointed Sanson Geographe Ordinaire du Roi. Sanson's duties in this coveted position included advising the king on matters of geography and compiling the royal cartographic archive. In 1644, he partnered with Pierre Mariette, an established print dealer and engraver, whose business savvy and ready capital enabled Sanson to publish an enormous quantity of maps. Sanson's corpus of some three hundred maps initiated the golden age of French mapmaking and he is considered the 'Father of French Cartography.' His work is distinguished as being the first of the 'Positivist Cartographers,' a primarily French school of cartography that valued scientific observation over historical cartographic conventions. The practice result of the is less embellishment of geographical imagery, as was common in the Dutch Golden Age maps of the 16th century, in favor of conventionalized cartographic representational modes. Sanson is most admired for his construction of the magnificent atlas Cartes Generales de Toutes les Parties du Monde. Sanson's maps of North America, Amerique Septentrionale (1650), Le Nouveau Mexique et La Floride (1656), and La Canada ou Nouvelle France (1656) are exceptionally notable for their important contributions to the cartographic perceptions of the New World. Both maps utilize the discoveries of important French missionaries and are among the first published maps to show the Great Lakes in recognizable form. Sanson was also an active proponent of the insular California theory, wherein it was speculated that California was an island rather than a peninsula. After his death, Sanson's maps were frequently republished, without updates, by his sons, Guillaume (1633 - 1703) and Adrien Sanson (1639 - 1718). Even so, Sanson's true cartographic legacy as a 'positivist geographer' was carried on by others, including Alexis-Hubert Jaillot, Guillaume De L'Isle, Gilles Robert de Vaugondy, and Pierre Duval. More by this mapmaker...
Pierre Mariette (1569 - 1657) was a French publisher and engraver active in Paris during the first half of the 19th century. Mariette established himself as successful publisher of art prints, but decided to turn his energy to cartography with the purchase of the plates for Melchior Tavernier's maps in 1644. Tavernier had partnered with Sanson before his death and Mariette followed suit. Around 1644- 1648 Mariette partnered with Nicolas Sanson, a then nascent figure in French cartography, to produce folio maps and atlases. The Sanson-Mariette relationship depended upon Sanson to draw and obtain rights for the maps while Mariette engraved them and paid for the expensive printing process. The two then shared rights to the maps into perpetuity. The finished copper plates were split between two such that neither could publish an atlas without the other's assent. The relationship seemed reasonably amicable until Mariette's death in 1657, when disputes arose between Sanson and Mariette's heirs. A court battle finally returned the most of the plates to Sanson's own heirs in 1674. As a consequence, some printings feature the Mariette imprint, others the Sanson imprint, and still others both imprints. Learn More...
Jean Pruthenus Somer (fl. 1650 - 1663), aka Sommer, also known as Jean Somers Pruthenus ('Pruthenus' means 'The Prussian'), was a Prussian engraver active in Paris in the middle part of the 17th century. Somer worked extensively for Sanson and Mariette, for whom he was the principal map engraver. His imprint appears on many of Sanson's most influential maps. Learn More...