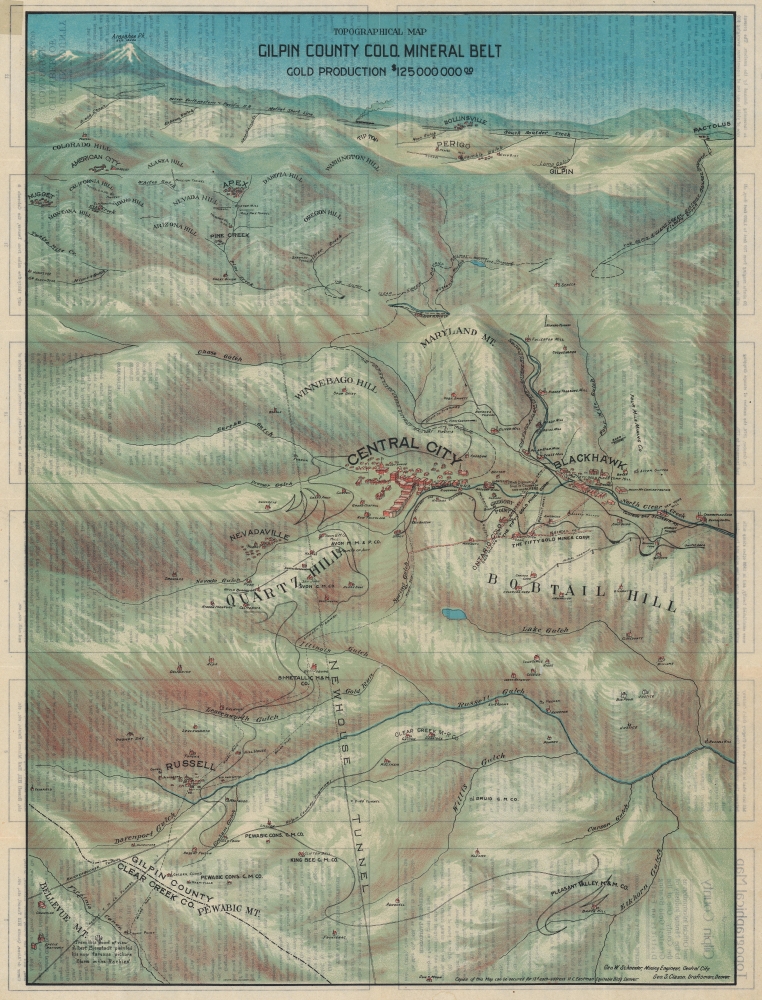
1906 Clason Bird's Eye View Topographical Map of Gilpin County, Colorado
GilpinCountyColorado-clason-1906
Title
1906 (undated) 24 x 17.5 in (60.96 x 44.45 cm)
Description
A Closer Look
Centered on Central City, this view extends as far north as Rollinsville and Arapahoe Peak, south as far as Bellevue Mountain, as far east as Randolph Mill, and west to Nugget. It chronicles the history of the Colorado Gold Rush and the development of the Central City region. The site where John H. Gregory first discovered gold is identified, along with the point where Albert Bierstadt painted his famous 'Storm in the Rockies,' various gold claims, waterways, proposed railroads, mills, and settlements. Numerous historic gold mining towns, including Blackhawk, Russell, Apex, American City, Nugget, Rollinsville, Perigo, Gilpin, and Pactolus, also appear.The Colorado Gold Rush and Central City
In January 1859, John H. Gregory discovered gold high in the Rocky Mountains near present-day Idaho Springs, near Denver. The subsequent gold rush brought as many as 40,000 people to Denver by 1859. Even by late September of that year, 2,000 prospectors were working a 6-square-mile area around Central City. By 1860, there were about 10,000 people living in and around Central City. By 1900, with mines nearly exhausted of gold, Central City's population had fallen to just over 3,000. Nevertheless, the Colorado Gold Rush was one of the richest in U.S. history and contributed significantly to the settling and development of Colorado in the mid to late 19th century.Chromolithography
Chromolithography, sometimes called oleography, is a color lithographic technique developed in the mid-19th century. The process uses multiple lithographic stones, one for each color, to yield a rich composite effect. Generally, a chromolithograph begins with a black basecoat upon which subsequent colors are layered. Some chromolithographs used 30 or more separate lithographic stones to achieve the desired effect. Chromolithograph color can be blended for even more dramatic results. The process became extremely popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries when it emerged as the dominant method of color printing. The vivid color chromolithography made it exceptionally effective for advertising and propaganda.Publication History and Census
This map was drafted by George W. Schneider and published by George S. Clason for the Gilpin County Chamber of Commerce. We note eight examples cataloged in OCLC: Yale University, the University of Wisconsin Milwaukee, Southern Methodist University, Texas Tech University, the University of Denver, the Denver Public Library, the Colorado School of Mines, and the University of California Los Angeles.CartographerS
George Samuel Clason (November 7, 1874 - 1957) was born in the city of Louisiana, Missouri in 1874. As a young man, Clason studied at the University of Nebraska before joining the United States Army in 1898 to fight in the Spanish American War. After the war, he moved to Denver, Colorado where in 1905 he founded the Clason Map Company, thus starting his lucrative publishing career. Clason initially focused on mining and mineral maps - capitalizing on the Colorado and Nevada mining industry, but quickly transitioned to railroad maps, city maps, and by the 1920s, road maps. As the company expanded, Clason opened a secondary office in Chicago, Illinois - then a rising map publishing center and railroad hub. At least one other satellite office was opened in Los Angeles. Among his many achievements, Clason is credited with producing the first modern road atlas of the United States. In the late 1920s, Clason also published a series of get-rich-quick pamphlets in the form of parables. The most famous of these is The Richest Man in Babylon. This tells the story of Arkad, a citizen of Babylon famed for his great wealth and generosity who shares his wit and wisdom with his fellow Babylonians. In 1949, Clason moved to Napa, California to retire and found a social club for retired gentlemen. More by this mapmaker...
George W. Schneider (18xx - 19xx) was an American mining engineer. Born in Denver, Schneider graduated from the Colorado School of Mines in 1894. After graduating from the School of Mines, Schneider went to Michigan and studied mine economics at the Atlantic Copper Mine. He was 'actively engaged' in mining in Gilpin County, Colorado, from 1895 until 1903, where he also served as the United States mineral surveyor, county engineer, city engineer of Black Hawk, and the consulting engineer for the Kansas-Burroughs Consolidation Company and the Concrete Mining Company. He was appointed Professor of Mining at the Colorado School of Mines in July 1911 and held the position until July 1913, when he was dismissed by the new administration because they thought he 'would be unable to work harmoniously with the rest of the faculty and with a member of the Board of Trustees'. That same year he directed the Mining section of the Colorado Industrial Exposition that was held in New York City from November 1st through 27th. By 1915 Schneider was operating a placer mine in Bolivia and became part of the Bolivia Gold Exploration Company, which was based out of Colorado. We have been unable to locate any definite records for Schneider after 1916, which is referenced correspondence between him and the President of the Bolivia Gold Exploration Company. Learn More...