This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
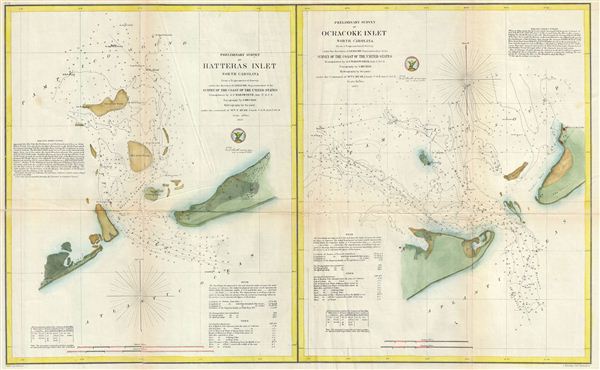
1857 U.S. Coast Survey Map of Hatteras Inlet and Ocracoke Inlet, North Carolina
HatterasInletOcracokeInlet-uscs-1857
Title
1857 (dated) 19 x 29 in (48.26 x 73.66 cm) 1 : 30000
Description
The triangulation upon which these charts were based is the work of A. S. Wadsworth. The topography for these charts was compiled by J. Mechan. The hydrography was accomplished by a party under the command of William T. Muse.
Cartographer
The Office of the Coast Survey (1807 - present) founded in 1807 by President Thomas Jefferson and Secretary of Commerce Albert Gallatin, is the oldest scientific organization in the U.S. Federal Government. Jefferson created the "Survey of the Coast," as it was then called, in response to a need for accurate navigational charts of the new nation's coasts and harbors. The spirit of the Coast Survey was defined by its first two superintendents. The first superintendent of the Coast Survey was Swiss immigrant and West Point mathematics professor Ferdinand Hassler. Under the direction of Hassler, from 1816 to 1843, the ideological and scientific foundations for the Coast Survey were established. These included using the most advanced techniques and most sophisticated equipment as well as an unstinting attention to detail. Hassler devised a labor intensive triangulation system whereby the entire coast was divided into a series of enormous triangles. These were in turn subdivided into smaller triangulation units that were then individually surveyed. Employing this exacting technique on such a massive scale had never before been attempted. Consequently, Hassler and the Coast Survey under him developed a reputation for uncompromising dedication to the principles of accuracy and excellence. Unfortunately, despite being a masterful surveyor, Hassler was abrasive and politically unpopular, twice losing congressional funding for the Coast Survey. Nonetheless, Hassler led the Coast Survey until his death in 1843, at which time Alexander Dallas Bache, a great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, took the helm. Bache was fully dedicated to the principles established by Hassler, but proved more politically astute and successfully lobbied Congress to liberally fund the endeavor. Under the leadership of A. D. Bache, the Coast Survey completed its most important work. Moreover, during his long tenure with the Coast Survey, from 1843 to 1865, Bache was a steadfast advocate of American science and navigation and in fact founded the American Academy of Sciences. Bache was succeeded by Benjamin Pierce who ran the Survey from 1867 to 1874. Pierce was in turn succeeded by Carlile Pollock Patterson who was Superintendent from 1874 to 1881. In 1878, under Patterson's superintendence, the U.S. Coast Survey was reorganized as the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey (C & GS) to accommodate topographic as well as nautical surveys. Today the Coast Survey is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or NOAA as the National Geodetic Survey. More by this mapmaker...