This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
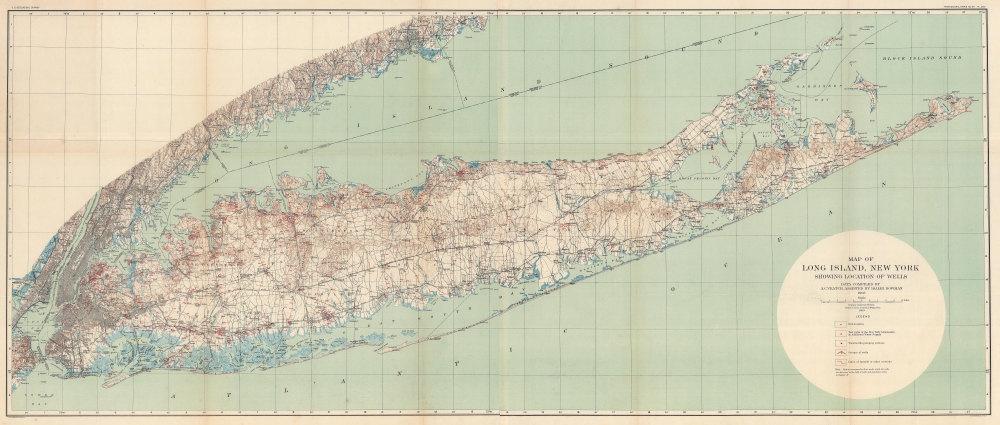
1904 U.S. Geological Survey of Long Island, New York
LongIsland-usgs-1904
Title
1904 (dated) 26.5 x 62 in (67.31 x 157.48 cm) 1 : 125000
Description
A Closer Look
Measuring an impressive 62-inches long, red squares, triangles, and other notations mark the wells, pumping stations, and other installations from Manhattan to Montauk. It highlights water wells, pumping stations, and other waterworks. Apart from these sites, Long Island's major roadways are illustrated, and streets in Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, the Bronx, and Jersey City appear. The Long Island Railroad runs from Hunter's Point to Greenport and Montauk. The Bay Ridge Railroad and the New York and Rockaway Beach Railroad are also depicted.Publication History and Census
This map was prepared in 1903 from data collected by A. C. Veatch and Isaiah Bowman. It was engraved and printed for the U.S. Geological Survey by Julius Bien, a well-known government and commercial printer based in New York City. The map was published in a vaguely titled government document referenced as 'Professional Paper no. 44.' This map is somewhat uncommon, with only one auction record in the past 10 years. We note 7 examples in OCLC: Brooklyn Public Library, Hofstra University, Stony Brook University, Yale University, the University of Connecticut, the University of California Los Angeles, and the University of California Berkeley.CartographerS
The Office of the Coast Survey (later the U.S. Geodetic Survey) (1807 - present), founded in 1807 by President Thomas Jefferson and Secretary of Commerce Albert Gallatin, is the oldest scientific organization in the U.S. Federal Government. Jefferson created the "Survey of the Coast," as it was then called, in response to a need for accurate navigational charts of the new nation's coasts and harbors. The first superintendent of the Coast Survey was Swiss immigrant and West Point mathematics professor Ferdinand Hassler. Under the direction of Hassler, from 1816 to 1843, the ideological and scientific foundations for the Coast Survey were established. Hassler, and the Coast Survey under him developed a reputation for uncompromising dedication to the principles of accuracy and excellence. Hassler lead the Coast Survey until his death in 1843, at which time Alexander Dallas Bache, a great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin, took the helm. Under the leadership A. D. Bache, the Coast Survey did most of its most important work. During his Superintendence, from 1843 to 1865, Bache was steadfast advocate of American science and navigation and in fact founded the American Academy of Sciences. Bache was succeeded by Benjamin Pierce who ran the Survey from 1867 to 1874. Pierce was in turn succeeded by Carlile Pollock Patterson who was Superintendent from 1874 to 1881. In 1878, under Patterson's superintendence, the U.S. Coast Survey was reorganized as the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey (C & GS or USGS) to accommodate topographic as well as nautical surveys. Today the Coast Survey is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or NOAA. More by this mapmaker...
Julius (Julien) Bien (September 27, 1826 - December 21, 1909) was a German-Jewish lithographer and engraver based in New York City. Bien was born in Naumburg, Germany. He was educated at the Academy of Fine Arts, Cassell and at Städel's Institute, Frankfurt-am-Main. Following the suppression of the anti-autocratic German Revolutions of 1848, Bien, who participated in the pan-German movement, found himself out of favor in his home country and joined the mass German immigration to the United States. Bien can be found in New York as early as 1849. He established the New York Lithographing, Engraving & Printing Company in New York that focused on the emergent chromo-lithograph process - a method of printing color using lithographic plates. His work drew the attention of the U.S. Government Printing Office which contracted him to produce countless government maps and surveys, including the Pacific Railroad Surveys, the census, numerous coast surveys, and various maps relating to the American Civil War. Bien also issued several atlases both privately and in conjunction with a relation, Joseph Bien. At the height of his career Bien was elected president of the American Lithographers Association. After his death in 1909, Bien's firm was taken over by his son who promptly ran it into insolvency. The firm was sold to Sheldon Franklin, who, as part of the deal, retained the right to publish under the Julius Bien imprint. In addition to his work as a printer, Bien was active in the New York German Jewish community. He was director of the New York Hebrew Technical Institute, the New York Hebrew Orphan Asylum, and president of the B'nai B'rith Order. Learn More...