This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
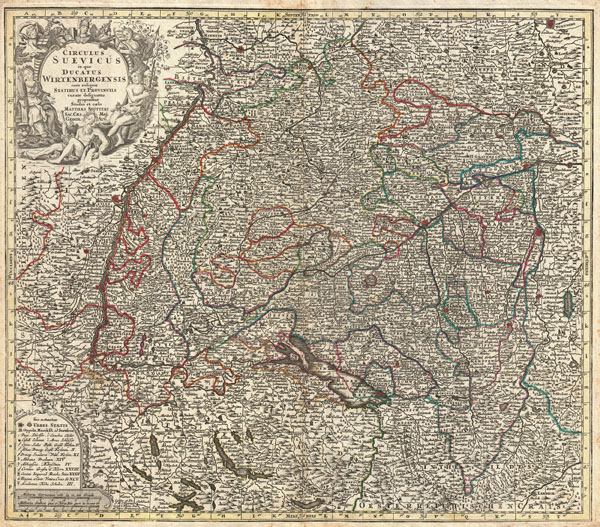
1740 Seutter Map of Swabia and Wirtenberg, Germany
Suevicus-seutter-1740
Title
c. 1740 (undated) 19.75 x 22.5 in (50.165 x 57.15 cm)
Description
CartographerS
Matthäus Seutter (1678 - 1757) was one of the most important and prolific German map publishers of the 18th century. Seutter was born the son of a goldsmith but apprenticed as a brewer. Apparently uninspired by the beer business, Seutter abandoned his apprenticeship and moved to Nuremberg where he apprenticed as an engraver under the tutelage of the prominent J. B. Homann. Sometime in the early 1700s Seutter left Homann to return to Augsburg, where he worked for the prominent art publisher Jeremiad Wolff (1663 - 1724), for whom he engraved maps and other prints. Sometime around 1717 he established his own independent cartographic publishing firm in Augsburg. Though he struggled in the early years of his independence, Seutter's engraving skill and commitment to diversified map production eventually attracted a substantial following. Most of Seutter's maps are heavily based upon, if not copies of, earlier work done by the Homann and De L'Isle firms. Nonetheless, by 1731/32 Seutter was one of the most prolific publishers of his time and was honored by the German Emperor Karl VI who gave him the title of Imperial Geographer, after which most subsequent maps included the Avec Privilege designation. Seutter continued to publish until his death, at the height of his career, in 1757. Seutter had two engraver sons, Georg Matthäus Seutter (1710 - 173?) and Albrecht Carl Seutter (1722 - 1762). Georg Matthäus quit the business and relocated to Woehrdt in 1729 (and probably died shortly thereafter), leaving the family inheritance to his wastrel brother Albrecht Carl Seutter, who did little to advance the firm until in own death in 1762. Following Albrecht's death, the firm was divided between the established Johann Michael Probst (1727 - 1776) firm and the emerging firm of Tobias Conrad Lotter. Lotter, Matthäus Seutter's son-in-law, was a master engraver and worked tirelessly on behalf of the Suetter firm. It is Lotter, who would eventually become one of the most prominent cartographers of his day, and his descendants, who are generally regarded as the true successors to Matthäus Seutter. (Ritter, M. Seutter, Probst and Lotter: An Eighteenth-Century Map Publishing House in Germany., "Imago Mundi", Vol. 53, (2001), pp. 130-135.) More by this mapmaker...
Johann Baptist Homann (March 20, 1664 - July 1, 1724) was the most prominent and prolific map publisher of the 18th century. Homann was born in Oberkammlach, a small town near Kammlach, Bavaria, Germany. As a young man, Homann studied in a Jesuit school and nursed ambitions of becoming a Dominican priest. Nonetheless, he converted to Protestantism in 1687, when he was 23. It is not clear where he mastered engraving, but we believe it may have been in Amsterdam. Homann's earliest work we have identified is about 1689, and already exhibits a high degree of mastery. Around 1691, Homann moved to Nuremberg and registered as a notary. By this time, he was already making maps, and very good ones at that. He produced a map of the environs of Nürnberg in 1691/92, which suggests he was already a master engraver. Around 1693, Homann briefly relocated to Vienna, where he lived and studied printing and copper plate engraving until 1695. Until 1702, he worked in Nuremberg in the map trade under Jacob von Sandrart (1630 - 1708) and then David Funck (1642 - 1709). Afterward, he returned to Nuremberg, where, in 1702, he founded the commercial publishing firm that would bear his name. In the next five years, Homann produced hundreds of maps and developed a distinctive style characterized by heavy, detailed engraving, elaborate allegorical cartouche work, and vivid hand color. Due to the lower cost of printing in Germany, the Homann firm could undercut the dominant French and Dutch publishing houses while matching their diversity and quality. Despite copious output, Homann did not release his first major atlas until the 33-map Neuer Atlas of 1707, followed by a 60-map edition of 1710. By 1715, Homann's rising star caught the attention of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI, who appointed him Imperial Cartographer. In the same year, he was also appointed a member of the Royal Academy of Sciences in Berlin. Homann's prestigious title came with several significant advantages, including access to the most up-to-date cartographic information as well as the 'Privilege'. The Privilege was a type of early copyright offered to very few by the Holy Roman Emperor. Though less sophisticated than modern copyright legislation, the Privilege offered limited protection for several years. Most all J. B. Homann maps printed between 1715 and 1730 bear the inscription 'Cum Priviligio' or some variation. Following Homann's death in 1724, the firm's map plates and management passed to his son, Johann Christoph Homann (1703 - 1730). J. C. Homann, perhaps realizing that he would not long survive his father, stipulated in his will that the company would be inherited by his two head managers, Johann Georg Ebersberger (1695 - 1760) and Johann Michael Franz (1700 - 1761), and that it would publish only under the name 'Homann Heirs'. This designation, in various forms (Homannsche Heirs, Heritiers de Homann, Lat Homannianos Herod, Homannschen Erben, etc.) appears on maps from about 1731 onwards. The firm continued to publish maps in ever-diminishing quantities until the death of its last owner, Christoph Franz Fembo (1781 - 1848). Learn More...