This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
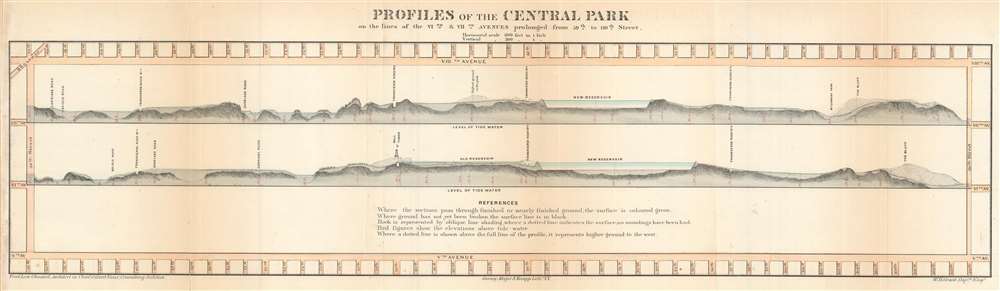
1860 Olmsted and Vaux Profile Chart or Map of Central Park, New York City
CentralParkProfiles-olmsted-1860
Title
1860 (undated) 7 x 24 in (17.78 x 60.96 cm) 1 : 7200
Description
New York's Central Park
Central Park, occupying central Manhattan from 59th to 110th streets, and from Central Park West to 5th Avenue, as built between 1857 and 1869. The park was designed the Landscape Architects, and indeed 'artists,' Vaux and Olmsted. Vaux and Olmsted were awarded the task of designing Central Park in 1853 by the City Common Council. Olmsted's vision drove the overall design while Vaux concentrated his attentions on bridges, buildings, and other structures within the park. The creation of Central Park, which was to consist of some 800 acres of public forest, pathways, promenades, lakes, bridges, and meadows, was a seminal moment in civic urban design. The park itself was designed as a whole with every tree, pond, and bench meticulously planned. Olmsted wrote: 'Every foot of the parks surface, every tree and bush, as well as every arch, roadway, and walk and been placed where it is for a purpose.'Historian Gloria Deak writes,
There was a staggering amount of work to be done to transform the area into a blend of pastoral and woodland scenery. This involved the design and construction of roadways, tunnels, bridges, arches, stairways, fountains, benches, lamp posts, gates, fences and innumerable other artifacts. It also involved the supervision of an army of about five thousand laborers…Olmsted, to whom most of the credit goes, insisted on seeing the multidimensional project as a single work of art, which he was mandated to create. For this purpose, he ventured to assume to himself the title of ‘artist.'Today, because of Vaux and Olmsted's efforts, New York Yorkers, ourselves included, have the privilege of enjoying what is, perhaps, the finest example of a planned urban public recreation area in the world.
Publication History and Census
This map was created by Olmsted and Vaux and lithographed by Sarony, Major and Knapp for publication in the Third Annual Report of the Board of Commissioners of the Central Park. The separate map is uncatalogued in OCLC, and only two examples of the report appear there. The report occasionally appears on the private market.CartographerS
Frederick Law Olmsted (April 26, 1822 - August 28, 1903) was an American journalist, landscape designer, and forefather of American landscape architecture. Born April 26, 1822 in Hartford, CT, Olmsted never attended college, instead taking work as a seaman, merchant, and journalist until 1848, when he settled at Tosomock Farm in Staten Island, New York. On June 13, 1859 Olmsted married Mary Cleveland, the widow of his brother John and adopted her three children. Olmsted’s fateful introduction to landscape design occurred in 1850, when a journalism assignment took him to England to visit public gardens. Inspired by Joseph Paxton's Birkenhead Park, he went on to write and publish Walks and Talks of an American Farmer in England. This led to additional work with the New York Daily Times (The New York Times) who sent him on an extensive tour through Texas and the American South from 1852 to 1857. It was after this trip that Olmsted wrote his popular criticism of slave economies, A Journey Through Texas. In 1858, Olmsted, along with his design partner, the architect Calvert Vaux, entered and won New York City's Central Park design competition. Though it was their first major landscape design project, the construction of Central Park from 1857 to 1866, created what many consider to be the finest planned urban recreation area in the world. They continued collaborating on such projects as Prospect Park in Brooklyn, Chicago's Riverside Park, the Buffalo park system, Milwaukee's Grand Necklace, and the Niagara Reservation. These were not just parks, but entire systems of parks and interconnecting parkways (which they invented) linking cities to green spaces. In 1883, Olmsted founded the Brookline, MA based Fairsted Company, the first landscape architecture firm in the United States. It was from this office he designed Boston's Emerald Necklace, the campus of Stanford University, the University of Chicago, the 1893 Columbian Exposition, and many other public areas. In 1895 Olmsted retired to Belmont, Massachusetts. Three years later, in 1898, he was admitted McLean Hospital, whose grounds he had designed several years before. He remained a resident and patient there until he passed away in 1903. Olmsted is buried in the Old North Cemetery, Hartford, Connecticut. More by this mapmaker...
Calvert Vaux (1824 - 1895) was a British architect and landscaper who is best remembered for his co-design, with Frederick Olmstead, of New York City's Central Park. Born in London in 1824, little is known of his early life, though it is recorded that, at 9 he was apprenticed to London architect Lewis Nockalls Cottingham, a proponent of the Gothic Revival Movement. Vaux worked for Cottingham until he was 26 years old, honing his skills and building a reputation as a skilled draftsman. During an exhibition of his watercolors in 1851, Vaux caught the attention of landscape designer Andrew Jackson Downing. Downing was looking for a partner to fulfill his revolutionary vision of urban architectural-landscaping. Dowing recruited Vaux to design buildings, bridges, and structures, while he focused on the overall landscape design. Vaux accompanied Downing to the United States where, in 1854, he gained U.S. citizenship and founded the American Institute of Architects. Vaux's partnership with Downing lasted approximately two years and resulted in a number of significant works, including the grounds of the White and Smithsonian Institute in Washington D.C. In 1852 Downing passed away in a tragic accident. At the time Downing was working on a landscape design for New York City's Central Park. In a decision that would forever change the American urban landscape, Vaux called in the fledgling landscape designer Frederick Olmstead to fill Downing shoes. Though Central Park was their first joint project, Vaux and Olmstead proved a magical combination, creating what many consider to be the finest planed urban recreation area in the world. Following the completion of Central Park, Vaux and Olmstead formed an official business partnership and went on to design Prospect Park in Brooklyn and Morningside Park in upper Manhattan. They planned one of the first suburbs in Chicago, Riverside, and were commissioned to design parks for Buffalo, NY, Milwaukee, WI, and Rockwood Park in Canada, among others. Vaux ended the partnership in 1872 and went on to collaborate with George Kent Radford and Samuel Parsons. However, in 1889 he again joined forces with Olmstead to design Downing Park, as a memorial to his mentor. Vaux tragically passed away on November 19, 1895, when he drowned in Brooklyn, NY. Learn More...
Napoleon Sarony (March 9, 1821 - November 9, 1896) was a dashingly handsome Canadian-American lithographer and publisher active in New York in the mid to late 19th century. Sarony was born in Quebec and emigrated to New York City in 1835. He apprenticed under Henry Robinson (fl. 1830/33 - 1850) before working as a lithograph artist for Nathaniel Currier (1813 - 1888). In 1846, he partnered with Currier's apprentice lithographer Henry B. Major to establish the firm of 'Sarony and Major.' From offices at 117 Futon Street, they published under this imprint until roughly 1853, when Sarony split off on his own under the imprint 'Sarony and Co.', still at 117 Fulton. At the time 'and Co.' probably meant Joseph Fairchild Knapp (1832 - 1891), Sarony's apprentice, and Richard C. Major, possibly Henry Major's son. In 1857, a new imprint was established as 'Sarony, Major and Knapp'. According to an advertisement in the New York Times (Feb 16, 1864), Sarony had invested in the business at founding, but was not an active partner, possibly because he was traveling in Europe. It is unclear why Sarony's name was maintained, possibly to capitalize on his fame, as a honorific, or possibly because he owned a major stake. They published under this imprint until 1863, becoming a major concern at 449 Broadway. Sarony's name was formally removed from the partnership in 1863. At the time he was traveling in Europe, mastering the most advanced color lithography and photographic techniques. He is known to have worked in France, Germany, and England. He returned to New York in the 1860s, establishing a photography company at 37 Union Square that became famous for its portraits of late-19th-century American theater icons. In 1891, Sarony, hoping to capitalize on Sarah Bernhardt's fame as 'Cleopatra', paid the stage actress 1,500 USD to sit for a photo session, the modern-day equivalent of 20,000 USD - suggesting a highly prosperous business. His son, Otto Sarony (1850–1903), continued the family business as a theater and film star photographer. As an aside, Sarony's second wife, Louie Sarony, was a known eccentric who would reportedly dress in elaborate rented costumes to walk around Washington Square each afternoon. Learn More...
Henry Broughman Major (February 17, 1820 - August 28, 1887) was an American lithographer based in New York in the middle to late 19th century. Major was born in Frome, England and emigrated to the United States in 1834. He apprenticed under Nathaniel Currier (1813 - 1888), befriending Currier lithographer Napoleon Sarony (1821 - 1896). Major worked briefly on his own, or perhaps with his cousin James Parsons Major, from 1845 - 1846 at 10 Watts Street. In 1846 he joined Sarony to found 'Sarony and Major', based at 117 Fulton Street, New York. Henry Major left the firm in 1853 for unknown reasons. At this time, a relative, possibly his son, Richard C. Major, continued to work with Sarony and Joseph Fairchild Knapp (1832 - 1891), creating the firm 'Sarony, Major and Knapp' (1857 - 1863). Learn More...
Joseph Fairchild Knapp (July 1, 1832 - September 14, 1891) was an American printer and publisher active in the second half of the 19th century. From the age of 16, Knapp apprenticed as a lithographer under Napoleon Sarony (1821 - 1896) and Henry B. Major (18?? - 18??), at the firm of 'Sarony and Major.' Henry Major either died or left the firm around 1853, with, possibly, his shares being held in reserve for his son, who was then still an apprentice, Richard C. Major. In 1857, Sarony left the firm to travel and study in Europe, Knapp and Richard Major took over the firm, becoming partners, renaming the business 'Sarony, Major and Knapp' (1857 - 1863). It is unclear why Sarony's name was maintained, possibly to capitalize on his fame, as a honorific, or possibly because he owned a major stake. Nonetheless, in 1863, Sarony, who had been absent for 7 years, was pushed out of the company which was was renamed 'Major and Knapp.' They published under this imprint from various locations over the years: 449 Broadway (1864 - 1866), 71 Broadway (1867 - 1872), and 56 Park Place (1889 - 1892). Richard Major retired in 1888, and the firm was renamed Knapp and Company. The firm grew to become one of the largest lithographic presses in the United States and a major force in American printing. Knapp invested some of his considerable wealth into insurance concerns. In 1868, he was the largest shareholder and director, and chairman of the Metropolitan Insurance Company. He became president of the Metropolitan Insurance Company in 1871, pioneering the idea of the low-cost life insurance policy, propelling MIC to become one of the largest insurers in the United States. All the time, he also continued to operate and manage his printing business, which he passed on to this son Joseph Palmer Knapp (1864 - 1951). Palmer Knapp closed 'Knapp and Company' in 1982, a year after his father's death, to establish the American Lithographic Company, which consolidated various smaller printers under a new imprint. Knapp constructed a large and elegant mansion in Brooklyn, which stood at 554 Bedford Avenue. Learn More...