This item has been sold, but you can get on the Waitlist to be notified if another example becomes available, or purchase a digital scan.
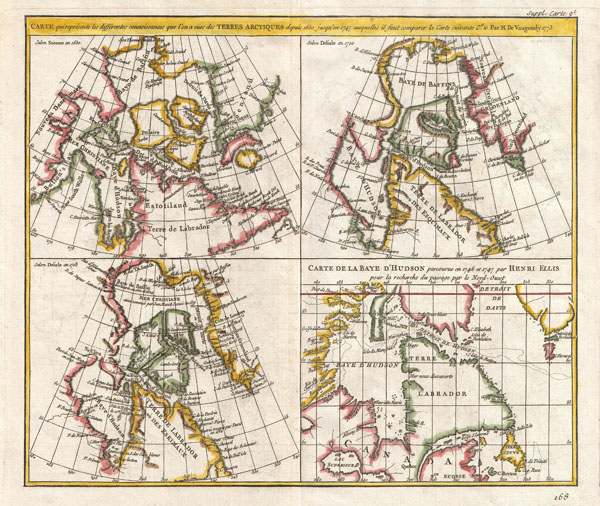
1772 Vaugondy - Diderot Map of the Hudson Bay and the Arctic
TerresArctiques-vaugondy-1773
Title
1773 (dated) 12 x 14 in (30.48 x 35.56 cm)
Description
Prepared by Vaugondy as plate no. 9 for the Supplement to Diderot's Encyclopédie.
CartographerS
Robert de Vaugondy (fl. c. 1716 - 1786) was French may publishing from run by brothers Gilles (1688 - 1766) and Didier (c. 1723 - 1786) Robert de Vaugondy. They were map publishers, engravers, and cartographers active in Paris during the mid-18th century. The father and son team were the inheritors to the important Nicolas Sanson (1600 - 1667) cartographic firm whose stock supplied much of their initial material. Graduating from Sanson's maps, Gilles, and more particularly Didier, began to produce their own substantial corpus. The Vaugondys were well-respected for the detail and accuracy of their maps, for which they capitalized on the resources of 18th-century Paris to compile the most accurate and fantasy-free maps possible. The Vaugondys compiled each map based on their own geographic knowledge, scholarly research, journals of contemporary explorers and missionaries, and direct astronomical observation. Moreover, unlike many cartographers of this period, they took pains to reference their sources. Nevertheless, even in 18th-century Paris, geographical knowledge was limited - especially regarding those unexplored portions of the world, including the poles, the Pacific Northwest of America, and the interiors of Africa, Australia, and South America. In these areas, the Vaugondys, like their rivals De L'Isle and Buache, must be considered speculative or positivist geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown lands with theories based on their knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered rivalries. Vaugondy's feuds with other cartographers, most specifically Phillipe Buache, resulted in numerous conflicting papers presented before the Academie des Sciences, of which both were members. The era of speculative cartography effectively ended with the late 18th-century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. After Didier died, his maps were acquired by Jean-Baptiste Fortin, who in 1787 sold them to Charles-François Delamarche (1740 - 1817). While Delamarche prospered from the Vaugondy maps, he defrauded Vaugondy's window Marie Louise Rosalie Dangy of her rightful inheritance and may even have killed her. More by this mapmaker...
Denis Diderot (October 5, 1713 - July 31, 1784) was a French Enlightenment era philosopher, publisher and writer. Diderot was born in the city of Langres, France and educated at the Lycée Louis le Grand where, in 1732, he earned a master of arts degree in philosophy. Diderot briefly considered careers in the clergy and in law, but in the end chose the more fiscally challenge course of a writer. Though well respected in philosophical circles Diderot was unable to obtain any of the government commissions that commonly supported his set and consequently spent much of his life in deep poverty. He is best known for his role in editing and producing the Encyclopédie . The Encyclopédie was one of the most revolutionary and impressive works of its time. Initially commissioned as a translation of Ephraim Chambers' Cyclopaedia, or Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences, Diderot instead turned into a much larger and entirely new work of monumental depth and scope. Diderot's Encyclopédie was intended to lay bare before the common man the intellectual mysteries of science, art and philosophy. This revolutionary mission was strongly opposed by the powers of the time who considered a learned middle class it a threat to their authority. In the course of the Encyclopédie production Diderot was imprisoned twice and the work itself was officially banned. Nonetheless, publication continued in response to a demand exceeding 4000 subscribers. The Encyclopédie was finally published in 1772 in 27 volumes. Following the publication of the Encyclopédie Diderot grew in fame but not in wealth. When the time came to dower his only surviving daughter, Angelique, Diderot could find no recourse save to sell his treasured library. In a move of largess, Catherine the II Russia sent an emissary to purchased the entire library on the condition that Diderot retain it in his possession and act as her "librarian" until she required it. When Diderot died of gastro-intestinal problems 1784, his heirs promptly sent his vast library to Catherine II who had it deposited at the Russian National Library, where it resides to this day. Learn More...
The De L'Isle family (fl. c. 1700 - c. 1760) (also written Delisle) were, in composite, a mapmaking tour de force who redefined early 18th century European cartography. Claude De L'Isle (1644 -1720), the family patriarch, was Paris based a historian and geographer under Nicholas Sanson. De L'Isle and his sons were proponents of the school of "positive geography" and were definitive figures, defining the heights of the Golden Age of French Cartography. Of his twelve sons, four, Guillaume (1675 - 1726), Simon Claude (1675 - 1726), Joseph Nicholas (1688 - 1768) and Louis (1720 - 1745), made a significant contributions to cartography. Without a doubt Guillaume was the most remarkable member of the family. It is said that Guillaume's skill as a cartographer was so prodigious that he drew his first map at just nine years of age. He was tutored by J. D. Cassini in astronomy, science, mathematics and cartography. By applying these diverse disciplines to the vast stores of information provided by 18th century navigators, Guillaume created the technique that came to be known as "scientific cartography", essentially an extension of Sanson's "positive geography". This revolutionary approach transformed the field of cartography and created a more accurate picture of the world. Among Guillaume's many firsts are the first naming of Texas, the first correct map of the Mississippi, the final rejection of the insular California fallacy, and the first identification of the correct longitudes of America. Stylistically De L'Isle also initiated important changes to the medium, eschewing the flamboyant Dutch style of the previous century in favor of a highly detailed yet still decorative approach that yielded map both beautiful and informative. Guillaume was elected to the French Academie Royale des Sciences at 27. Later, in 1718, he was also appointed "Premier Geographe du Roi", an office created especially for him. De L'Isle personally financed the publication of most of his maps, hoping to make heavy royalties on their sales. Unfortunately he met an untimely death in 1728, leaving considerable debt and an impoverished child and widow. De L'Isle's publishing firm was taken over by his assistant, Phillipe Buache who became, posthumously, his son in law. The other De L'Isle brothers, Joseph Nicholas and Louis De L'Isle, were employed in the Service of Peter the Great of Russia as astronomers and surveyors. They are responsible for cataloguing and compiling the data obtained from Russian expeditions in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America, including the seminal explorations of Vitus Bering and Aleksei Chirikov. The De L'Isles, like their rivals the Vaugondys , must be considered speculative geographers. Speculative geography was a genre of mapmaking that evolved in Europe, particularly Paris, in the middle to late 18th century. Cartographers in this genre would fill in unknown areas on their maps with speculations based upon their vast knowledge of cartography, personal geographical theories, and often dubious primary source material gathered by explorers and navigators. This approach, which attempted to use the known to validate the unknown, naturally engendered many rivalries. The era of speculatively cartography effectively ended with the late 18th century explorations of Captain Cook, Jean Francois de Galaup de La Perouse, and George Vancouver. Learn More...